Page 25 - FINAL CFA II SLIDES JUNE 2019 DAY 8
P. 25
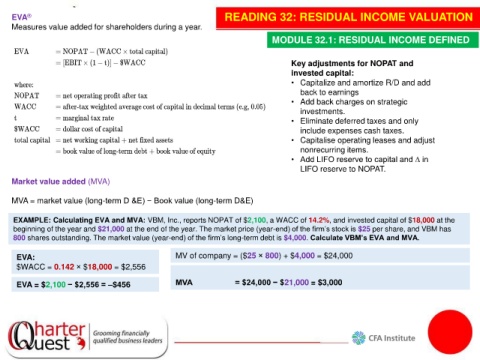
EVA ® READING 32: RESIDUAL INCOME VALUATION
Measures value added for shareholders during a year.
MODULE 32.1: RESIDUAL INCOME DEFINED
Key adjustments for NOPAT and
invested capital:
• Capitalize and amortize R/D and add
back to earnings
• Add back charges on strategic
investments.
• Eliminate deferred taxes and only
include expenses cash taxes.
• Capitalise operating leases and adjust
nonrecurring items.
• Add LIFO reserve to capital and ∆ in
LIFO reserve to NOPAT.
Market value added (MVA)
MVA = market value (long-term D &E) − Book value (long-term D&E)
EXAMPLE: Calculating EVA and MVA: VBM, Inc., reports NOPAT of $2,100, a WACC of 14.2%, and invested capital of $18,000 at the
beginning of the year and $21,000 at the end of the year. The market price (year-end) of the firm’s stock is $25 per share, and VBM has
800 shares outstanding. The market value (year-end) of the firm’s long-term debt is $4,000. Calculate VBM’s EVA and MVA.
EVA: MV of company = ($25 × 800) + $4,000 = $24,000
$WACC = 0.142 × $18,000 = $2,556
EVA = $2,100 − $2,556 = –$456 MVA = $24,000 − $21,000 = $3,000