Page 288 - PM Integrated Workbook 2018-19
P. 288
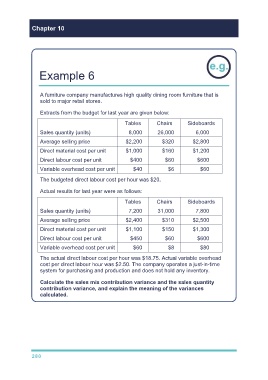
Chapter 10
Example 6
A furniture company manufactures high quality dining room furniture that is
sold to major retail stores.
Extracts from the budget for last year are given below:
Tables Chairs Sideboards
Sales quantity (units) 8,000 26,000 6,000
Average selling price $2,200 $320 $2,800
Direct material cost per unit $1,000 $160 $1,200
Direct labour cost per unit $400 $60 $600
Variable overhead cost per unit $40 $6 $60
The budgeted direct labour cost per hour was $20.
Actual results for last year were as follows:
Tables Chairs Sideboards
Sales quantity (units) 7,200 31,000 7,800
Average selling price $2,400 $310 $2,500
Direct material cost per unit $1,100 $150 $1,300
Direct labour cost per unit $450 $60 $600
Variable overhead cost per unit $60 $8 $80
The actual direct labour cost per hour was $18.75. Actual variable overhead
cost per direct labour hour was $2.50. The company operates a just-in-time
system for purchasing and production and does not hold any inventory.
Calculate the sales mix contribution variance and the sales quantity
contribution variance, and explain the meaning of the variances
calculated.
280