Page 121 - Microsoft Word - 00 Prelims.docx
P. 121
Pricing
The optimum price of a product
This is a general set of rules that can be applied to most questions involving algebra
and pricing.
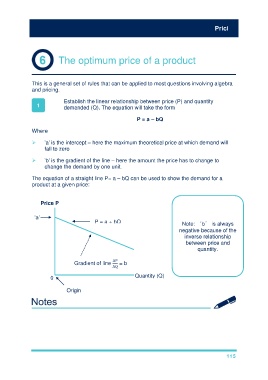
Establish the linear relationship between price (P) and quantity
1 demanded (Q). The equation will take the form
P = a – bQ
Where
'a' is the intercept – here the maximum theoretical price at which demand will
fall to zero
'b' is the gradient of the line – here the amount the price has to change to
change the demand by one unit.
The equation of a straight line P= a – bQ can be used to show the demand for a
product at a given price:
Price P
‘a’
P = a + bQ Note: ‘b’ is always
negative because of the
inverse relationship
between price and
quantity.
ΔP
Gradient of line = b
ΔQ
0 Quantity (Q)
Origin
115