Page 10 - PowerPoint Presentation
P. 10
LOS 7.d: Distinguish between the dependent and MODULE 7.2: LINEAR REGRESSION: INTRODUCTION
independent variables in a linear regression.
In a general form straight line equation: Y = a + bX, Y is the Dependent variable (also called the explained, endogenous, or the predicted
variable) and X is the Independent variable (also called the explanatory variable, exogenous, or predicting variable).
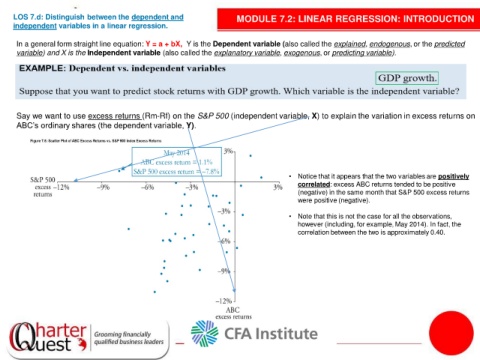
Say we want to use excess returns (Rm-Rf) on the S&P 500 (independent variable, X) to explain the variation in excess returns on
ABC’s ordinary shares (the dependent variable, Y).
• Notice that it appears that the two variables are positively
correlated: excess ABC returns tended to be positive
(negative) in the same month that S&P 500 excess returns
were positive (negative).
• Note that this is not the case for all the observations,
however (including, for example, May 2014). In fact, the
correlation between the two is approximately 0.40.