Page 40 - PowerPoint Presentation
P. 40
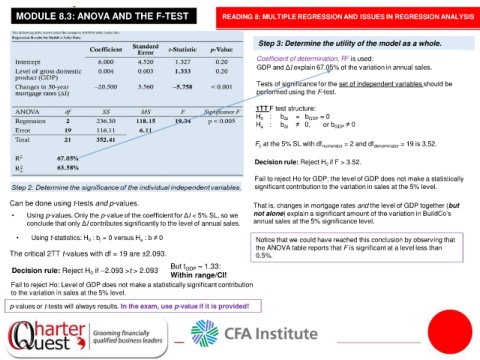
MODULE 8.3: ANOVA AND THE F-TEST READING 8: MULTIPLE REGRESSION AND ISSUES IN REGRESSION ANALYSIS
Step 3: Determine the utility of the model as a whole.
Coefficient of determination, R is used:
2,
GDP and ΔI explain 67.05% of the variation in annual sales.
Tests of significance for the set of independent variables should be
performed using the F-test.
1TT F test structure:
H 0 : b ΔI = b GDP = 0
H a : b ΔI ≠ 0, or b GDP ≠ 0
F at the 5% SL with df numerator = 2 and df denominator = 19 is 3.52.
c
Decision rule: Reject H if F > 3.52.
0
Fail to reject Ho for GDP; the level of GDP does not make a statistically
significant contribution to the variation in sales at the 5% level.
Can be done using t-tests and p-values. That is, changes in mortgage rates and the level of GDP together (but
• Using p-values. Only the p-value of the coefficient for ΔI < 5% SL, so we not alone) explain a significant amount of the variation in BuildCo’s
conclude that only ΔI contributes significantly to the level of annual sales. annual sales at the 5% significance level.
• Using t-statistics: H : b = 0 versus H : b ≠ 0 Notice that we could have reached this conclusion by observing that
j
0
a
the ANOVA table reports that F is significant at a level less than
The critical 2TT t-values with df = 19 are ±2.093. 0.5%.
But t = 1.33:
GDP
Decision rule: Reject H if –2.093 >t > 2.093 Within range/CI!
0
Fail to reject Ho: Level of GDP does not make a statistically significant contribution
to the variation in sales at the 5% level.
p-values or t-tests will always results. In the exam, use p-value if it is provided!