Page 3 - 091math-wb-w1-(Vector)
P. 3
WORKBOOK
VECTORS
1. Vectors
A vector is a directed line segment which has both magnitude (length) and direction. A vector in
plane has tail (initial point), a head (terminal point), direction and length.
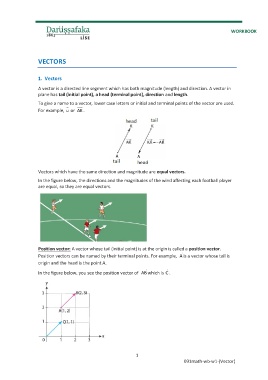
To give a name to a vector, lower case letters or initial and terminal points of the vector are used.
For example, u or AK .
Vectors which have the same direction and magnitude are equal vectors.
In the figure below, the directions and the magnitudes of the wind affecting each football player
are equal, so they are equal vectors.
Position vector: A vector whose tail (initial point) is at the origin is called a position vector.
Position vectors can be named by their terminal points. For example, A is a vector whose tail is
origin and the head is the point A.
In the figure below, you see the position vector of AB which is C .
1
091math-wb-w1-(Vector)