Page 8 - WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES- BLUETOOTH AND WI-FI
P. 8
A.2 Classification of Bluetooth
Bluetooth devices may have different RF power classification levels. The power versions for
Bluetooth include; 1 mW - class 3, 2.5 mW - class 2, and 100 mWatts - class 1.
Devices that have an extremely low power level of 1 milliwatt have a very short range of
approximately 1 meter. Bluetooth devices that have a power level of up to 100 milliwatts can
provide a transmission range of approximately to 100 meters. The high power version (class 1) is
required to use adjustable (dynamic) power control that automatically is reduced when enough
signal strength is available between Bluetooth devices.
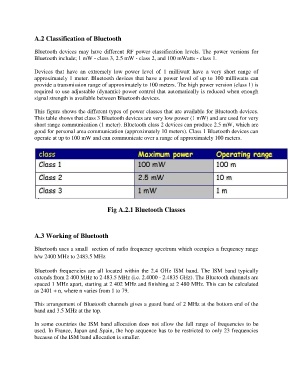
This figure shows the different types of power classes that are available for Bluetooth devices.
This table shows that class 3 Bluetooth devices are very low power (1 mW) and are used for very
short range communication (1 meter). Bluetooth class 2 devices can produce 2.5 mW, which are
good for personal area communication (approximately 10 meters). Class 1 Bluetooth devices can
operate at up to 100 mW and can communicate over a range of approximately 100 meters.
Fig A.2.1 Bluetooth Classes
A.3 Working of Bluetooth
Bluetooth uses a small section of radio frequency spectrum which occupies a frequency range
b/w 2400 MHz to 2483.5 MHz
Bluetooth frequencies are all located within the 2.4 GHz ISM band. The ISM band typically
extends from 2 400 MHz to 2 483.5 MHz (i.e. 2.4000 - 2.4835 GHz). The Bluetooth channels are
spaced 1 MHz apart, starting at 2 402 MHz and finishing at 2 480 MHz. This can be calculated
as 2401 + n, where n varies from 1 to 79.
This arrangement of Bluetooth channels gives a guard band of 2 MHz at the bottom end of the
band and 3.5 MHz at the top.
In some countries the ISM band allocation does not allow the full range of frequencies to be
used. In France, Japan and Spain, the hop sequence has to be restricted to only 23 frequencies
because of the ISM band allocation is smaller.