Page 13 - herina surgery and possible lawsuits
P. 13
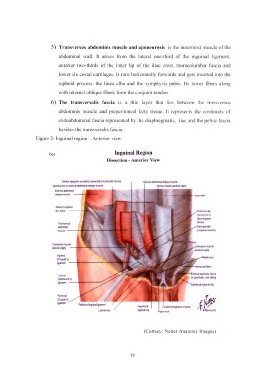
5) Transversus abdominis muscle and aponeurosis is the innermost muscle of the
abdominal wall. It arises from the lateral one-third of the inguinal ligament,
anterior two-thirds of the inner lip of the iliac crest, thoracolumbar fascia and
lower six costal cartilages. It runs horizontally forwards and gets inserted into the
xiphoid process, the linea alba and the symphysis pubis. Its lower fibers along
with internal oblique fibers form the conjoint tendon.
6) The transversalis fascia is a thin layer that lies between the transversus
abdominis muscle and preperitoncal fatty tissue. It represents the continuity of
endoabdominal fascia represented by the diaphragmatic, iliac and the pelvic fascia
besides the transversalis fascia.
Figure 2: Inguinal region - Anterior view
ber Inguinal Region
Dissection - Anterior View
Inferior epigastric vessels (covered bg transversalis fascia) Internal abdominal oblique muscle
Aponeurosis of external abdominal oblique muscle lectus sheath (anterior layer)
External abdominal
oblique muscle
Anterior superior
iliac spine Transversalis
fascia (site of
direct inguinal
hernia)
Transversus
abdominis fa lx inguinaiis
(conformed tendon)
muscle —
Cremaster muscle
Remaster muscle
(lateral origin)
(medial origin |
Inguinal
ial crus
(Poupart’s)
ligament ■
Hntercrural fibers
External spermatic fascia
Lacunar
on spermatic cord exiting
(Gimbernat's
ligament ~
:ial inguinal ring
Pectineal
(Cooper's)
ligament
Reflected inguinal ligament
Superficial Fundiform ligament of penis
Lateral crus inguinal ring I ® Novartis
Pubic crest
(Curtsey: Netter Anatomy Images)
19