Page 27 - herina surgery and possible lawsuits
P. 27
1 Diagnosis of inguinal hernia .
The symptoms and signs vary with the type, size, duration, and presence or absence of
complications. Indirect hernias generally present in infancy or during the first year of life.
Clinical features:
1. Symptoms-
a) Swelling in mgmnoscrotal region - In adult life the hernia discovered
accidentally by the patient or discovered by the physician during routine
examination. In certain cases the swelling appears after sudden severe strain.
b) Pain- It generally is a dragging pain when hernia is developing or expanding
in size, which is relieved with rest but increases after activity. Some time it
may be of dullache. The pain may be severe and continuous if hernia is
associated with complications.
2. Signs- the inguinal hernia usually diagnosed on physical examination.
• A globular or pyriform swelling, with an expansile cough impulse, which
generally reducible is almost diagnostic of hernia.
• Direct (medial) hernia arises from the posterior wall of the inguinal canal
while indirect hernia arises from the deep ring.
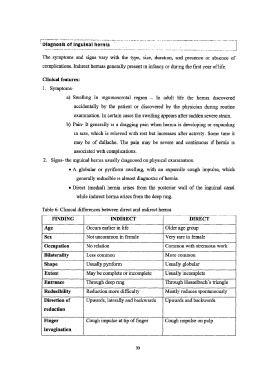
Table 6: Clinical differences between direct and indirect hernia
FINDING INDIRECT DIRECT
Age Occurs earlier in life Older age group
Sex Not uncommon in female Very rare in female
Occupation No relation Common with strenuous work
Bilaterality Less common More common
Shape Usually pyriform Usually globular
Extent May be complete or incomplete Usually incomplete
Entrance Through deep ring Through Hasselbach's triangle
Deducibility Reduction more difficulty Mostly reduces spontaneously
Direction of Upwards, laterally and backwards Upwards and backwards
reduction
Finger Cough impulse at tip of finger Cough impulse on pulp
invagination
33