Page 108 - C:\Users\msi\OneDrive\Documents\Flip PDF Corporate Edition\E-Commerce\
P. 108
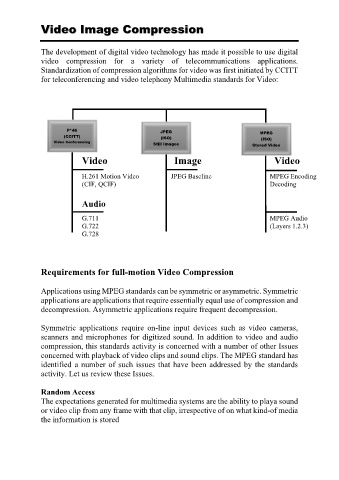
Video Image Compression
The development of digital video technology has made it possible to use digital
video compression for a variety of telecommunications applications.
Standardization of compression algorithms for video was first initiated by CCITT
for teleconferencing and video telephony Multimedia standards for Video:
P*46
(CCITT) JPEG MPEG
(ISO)
Video Conferencing Still Images (ISO)
Stored Video
Video Image Video
H.261 Motion Video JPEG Baseline MPEG Encoding
(CIF, QCIF) Decoding
Audio
G.711 MPEG Audio
G.722 (Layers 1.2.3)
G.728
Requirements for full-motion Video Compression
Applications using MPEG standards can be symmetric or asymmetric. Symmetric
applications are applications that require essentially equal use of compression and
decompression. Asymmetric applications require frequent decompression.
Symmetric applications require on-line input devices such as video cameras,
scanners and microphones for digitized sound. In addition to video and audio
compression, this standards activity is concerned with a number of other Issues
concerned with playback of video clips and sound clips. The MPEG standard has
identified a number of such issues that have been addressed by the standards
activity. Let us review these Issues.
Random Access
The expectations generated for multimedia systems are the ability to playa sound
or video clip from any frame with that clip, irrespective of on what kind-of media
the information is stored