Page 360 - 00. Complete Version - Progress Report IPEN 2014-2016
P. 360
360 Nuclear Safety | Progress Report
generating facility to estimate the radionuclide content of the waste. These methods are used
complementarily aiming at expediting the determinations, keeping the costs as low as possi-
ble and producing the more accurate and precise results achievable.
Some of the radiologically significant radionuclides emit low energy or less penetrating radia-
tions or are present in very low concentrations, which make the determination of the activities
a lengthy and complex task. These radionuclides are called Difficult-To-Measure (DTM) and are
the object of development of analytical methods worldwide. They are usually determined by
the method of Scaling Factors and Correlation Functions that allows estimating their concen-
trations as a proportion of the activity of radionuclides that are easily measured by radiomet-
ric methods, which are strong gamma emitters, called Key Nuclides (KN).
The research and development work performed by the GRR staff on the radioisotopic charac-
terization of the waste from the IEA-R1 reactor aims at establishing the analysis protocols, cre-
ating the instrumental infrastructure and training skilled analysts to perform the job.
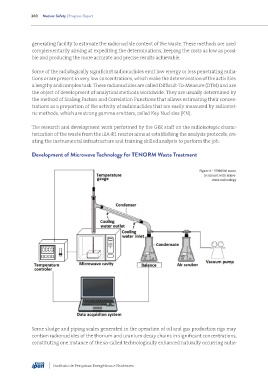
Development of Microwave Technology for TENORM Waste Treatment
Figure 3 – TENORM waste
treatment with micro-
wave technology
Some sludge and piping scales generated in the operation of oil and gas production rigs may
contain radionuclides of the thorium and uranium decay chains in significant concentrations,
constituting one instance of the so-called technologically enhanced naturally occurring radio-
Instituto de Pesquisas Energéticas e Nucleares