Page 29 - 22 Cotton SA magazine
P. 29
/ QUALITY CONTROL AND STANDARDS
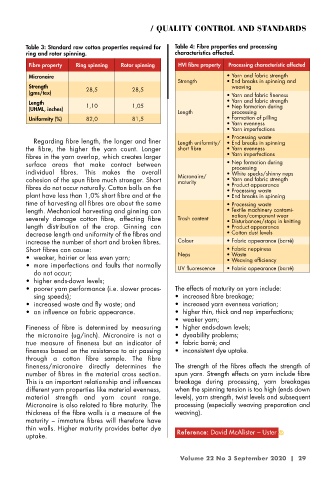
Table 3: Standard raw cotton properties required for Table 4: Fibre properties and processing
ring and rotor spinning. characteristics affected.
Fibre property Ring spinning Rotor spinning HVI fibre property Processing characteristic affected
Micronaire • Yarn and fabric strength
Strength • End breaks in spinning and
Strength 28,5 28,5 weaving
(gms/tex) • Yarn and fabric fineness
Length • Yarn and fabric strength
(UHML, inches) 1,10 1,05 • Nep formation during
Length processing
Uniformity (%) 82,0 81,5 • Formation of pilling
• Yarn evenness
• Yarn imperfections
• Processing waste
Regarding fibre length, the longer and finer Length uni formity/ • End breaks in spinning
the fibre, the higher the yarn count. Longer short fibre • Yarn evenness
fibres in the yarn overlap, which creates larger • Yarn imperfections
surface areas that make contact between • Nep formation during
processing
individual fibres. This makes the overall • White specks/shinny neps
cohesion of the spun fibre much stronger. Short Micronaire/ • Yarn and fabric strength
maturity
fibres do not occur naturally. Cotton bolls on the • Product appearance
• Processing waste
plant have less than 1,0% short fibre and at the • End breaks in spinning
time of harvesting all fibres are about the same • Processing waste
length. Mechanical harvesting and ginning can • Textile machinery contami-
nation/component wear
severely damage cotton fibre, affecting fibre Trash content • Disturbances/stops in knitting
length distribution of the crop. Ginning can • Product appearance
decrease length and uniformity of the fibres and • Cotton dust levels
increase the number of short and broken fibres. Colour • Fabric appearance (barré)
Short fibres can cause: • Fabric neppiness
• weaker, hairier or less even yarn; Neps • Waste
• Weaving efficiency
• more imperfections and faults that normally UV fluorescence • Fabric appearance (barré)
do not occur;
• higher ends-down levels;
• poorer yarn performance (i.e. slower proces- The effects of maturity on yarn include:
sing speeds); • increased fibre breakage;
• increased waste and fly waste; and • increased yarn evenness variation;
• an influence on fabric appearance. • higher thin, thick and nep imperfections;
• weaker yarn;
Fineness of fibre is determined by measuring • higher ends-down levels;
the micronaire (ug/inch). Micronaire is not a • dyeability problems;
true measure of fineness but an indicator of • fabric barré; and
fineness based on the resistance to air passing • inconsistent dye uptake.
through a cotton fibre sample. The fibre
fineness/micronaire directly determines the The strength of the fibres affects the strength of
number of fibres in the material cross section. spun yarn. Strength effects on yarn include fibre
This is an important relationship and influences breakage during processing, yarn breakages
different yarn properties like material evenness, when the spinning tension is too high (ends down
material strength and yarn count range. levels), yarn strength, twist levels and subsequent
Micronaire is also related to fibre maturity. The processing (especially weaving preparation and
thickness of the fibre walls is a measure of the weaving).
maturity – immature fibres will therefore have
thin walls. Higher maturity provides better dye
uptake. Reference: David McAlister – Uster
Volume 22 No 3 September 2020 | 29