Page 248 - C:\Users\azizu\Documents\Flip PDF Professional\Matematics-Form-1-1\
P. 248
1
(d) Area = × product of the lengths of the two diagonals
2
1 1
= × (3 + 2) × (2 + 2) × length of long diagonal × length of short diagonal
2 2
1
= × 5 × 4
2
= 10 cm
2
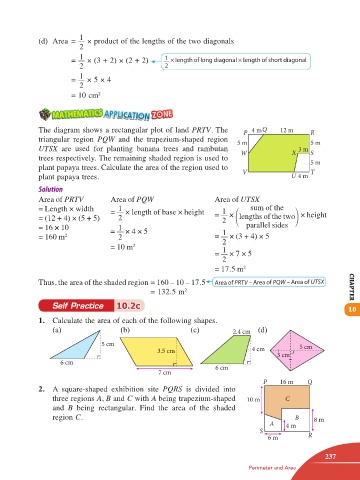
The diagram shows a rectangular plot of land PRTV. The P 4 m Q 12 m R
triangular region PQW and the trapezium-shaped region 5 m 5 m
UTSX are used for planting banana trees and rambutan W X 3 m S
trees respectively. The remaining shaded region is used to 5 m
plant papaya trees. Calculate the area of the region used to V T
plant papaya trees. U 4 m
Area of PRTV Area of PQW Area of UTSX
1
= Length × width = × length of base × height 1 sum of the
2 1
= (12 + 4) × (5 + 5) 2 = × lengths of the two 2 × height
= 16 × 10 = × 4 × 5 1 parallel sides
1
= 160 m 2 2 = × (3 + 4) × 5
2
= 10 m 2 1
= × 7 × 5
2
= 17.5 m 2
Thus, the area of the shaded region = 160 – 10 – 17.5 Area of PRTV – Area of PQW – Area of UTSX
= 132.5 m 2 CHAPTER
Self Practice 10.2c 10
1. Calculate the area of each of the following shapes.
(a) (b) (c) 2.4 cm (d)
5 cm 5 cm
3.5 cm 4 cm
3 cm
6 cm
7 cm 6 cm
P 16 m Q
2. A square-shaped exhibition site PQRS is divided into
three regions A, B and C with A being trapezium-shaped 10 m C
and B being rectangular. Find the area of the shaded
region C. B 8 m
A 4 m
S
6 m R
237
Perimeter and Area
10 TB Math F1.indd 237 11/10/16 12:19 PM