Page 307 - C:\Users\azizu\Documents\Flip PDF Professional\Matematics-Form-1-1\
P. 307
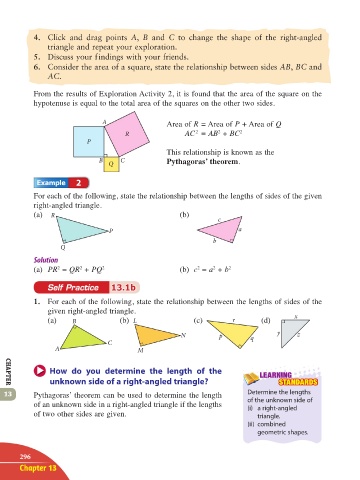
4. Click and drag points A, B and C to change the shape of the right-angled
triangle and repeat your exploration.
5. Discuss your f indings with your friends.
6. Consider the area of a square, state the relationship between sides AB, BC and
AC.
From the results of Exploration Activity 2, it is found that the area of the square on the
hypotenuse is equal to the total area of the squares on the other two sides.
A Area of R = Area of P + Area of Q
R AC = AB + BC 2
2
2
P
This relationship is known as the
B Q C Pythagoras’ theorem.
2
For each of the following, state the relationship between the lengths of sides of the given
right-angled triangle.
(a) R (b)
c
P a
b
Q
2
2
(a) PR = QR + PQ 2 (b) c = a + b 2
2
2
Self Practice 13.1b
1. For each of the following, state the relationship between the lengths of sides of the
given right-angled triangle.
(a) B (b) L (c) r (d) x
N p q y z
C
A M
How do you determine the length of the LEARNING
unknown side of a right-angled triangle? STANDARDS
CHAPTER
13 Pythagoras’ theorem can be used to determine the length Determine the lengths
of an unknown side in a right-angled triangle if the lengths of the unknown side of
(i) a right-angled
of two other sides are given. triangle.
(ii) combined
geometric shapes.
296
Chapter 13
13 TB Math F1.indd 296 11/10/16 12:22 PM