Page 93 - C:\Users\azizu\Documents\Flip PDF Professional\Matematics-Form-1-1\
P. 93
5
State the rate and the two quantities (including the units) involved in each of the following
situations.
(a) Fatin buys 2 kg of mangoes at the total price of RM10.
(b) A car consumes 1 litre of petrol for a distance of 12 km.
RM10 12 km
(a) Rate = (b) Rate =
2 kg 1 litre
The two quantities involved are mass The two quantities involved are
(kg) and total amount of money (RM). distance (km) and volume (litre).
CHAPTER
4
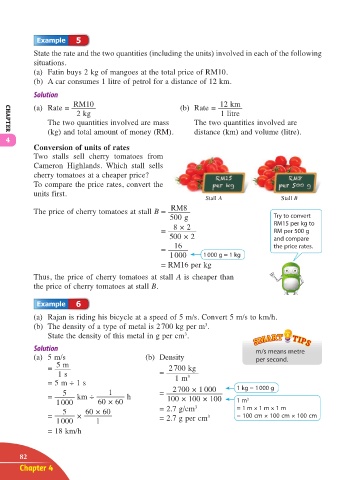
Conversion of units of rates
Two stalls sell cherry tomatoes from
Cameron Highlands. Which stall sells
cherry tomatoes at a cheaper price?
To compare the price rates, convert the
units first.
Stall A Stall B
RM8
The price of cherry tomatoes at stall B =
500 g Try to convert
RM15 per kg to
8 × 2
= RM per 500 g
500 × 2 and compare
16 the price rates.
=
1 000 1 000 g = 1 kg
= RM16 per kg
Thus, the price of cherry tomatoes at stall A is cheaper than
the price of cherry tomatoes at stall B.
6
(a) Rajan is riding his bicycle at a speed of 5 m/s. Convert 5 m/s to km/h.
(b) The density of a type of metal is 2 700 kg per m .
3
State the density of this metal in g per cm .
3
m/s means metre
(a) 5 m/s (b) Density per second.
5 m
= 2 700 kg
1 s = 1 m 3
= 5 m ÷ 1 s 1 kg = 1 000 g
5 1 = 2 700 × 1 000
= km ÷ h 100 × 100 × 100 1 m
3
1 000 60 × 60
3
5 60 × 60 = 2.7 g/cm = 1 m × 1 m × 1 m
= × = 2.7 g per cm = 100 cm × 100 cm × 100 cm
3
1 000 1
= 18 km/h
82
Chapter 4
04 TB Math F1.indd 82 11/10/16 12:12 PM