Page 67 - EM BIOLOGY NOTES 10TH CLASS PSR DIGITAL BOOKS
P. 67
DRAWING DIAGRAMS - PARTS - PROCEDURE
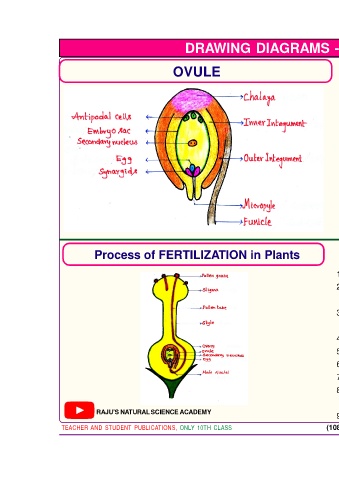
OVULE Structure of Ovule
1. An ovule is an egg-shaped structure attached by a stalk
to the inner side of the ovary.
2. Depending upon the species of plant involved, an ovary may
have one, two, several or even hundreds of ovules.
3. In the centre of the each ovule contains a microscopic embryo sac.
4. It surrounded by two integument : They are
1. Outer integument 2. Inner integument
5. The basal part of the ovule is called chalaza from chalaza the two integu-
ments are airse.
6. The two integuments leave a small pore opposite side of the chalaza is
called Micropyle.
7. They are total of 7 cells are arranged in three groups of embryo sac. They are :
1 egg, 2 synergids/helper cells
1 secondary nucleus, 3 Antipodal cells.
8. All cells in embryo sac are in haploid state (n) except secondary nucleus. It
is in diploid state (2n).
Process of FERTILIZATION in Plants DOUBLE Fertilization in plants
1. Fusion of male and female gamates is called Fertilization.
How to draw
2. For Fertilization, pollen grains have to reach the surface of the pl. scan QR
stigma is called Pollination.
3. Cells on the surface of the stigma secrets a sticky nutrient fluid contains sugar
and other substances.
4. This will help the pollengrains to germinate. Then it forms pollen tube.
5. Pollen tube travels through style and reaches ovary and enters into ovule through micropyle.
6. Pollen tube contains two male nuclei. These are enter into embryo sac.
7. One male nucleus fuses with egg to form a diploid (2n) cell called Zygote.
8. The other male nucleus fuses with secondary nucleus to form a triploid (3n)
endo spermal nucleus.
RAJU’S NATURAL SCIENCE ACADEMY
9. After fertilization ovary is converted into a fruit and the ovules into seed.
TEACHER AND STUDENT PUBLICATIONS, ONLY 10TH CLASS (108) PSR DIGITAL BOOKS (ONLINE&OFFLINE), ALL SUBJECTS (TM&EM) 9885678410