Page 405 - Board Member Onboardin August 2019
P. 405
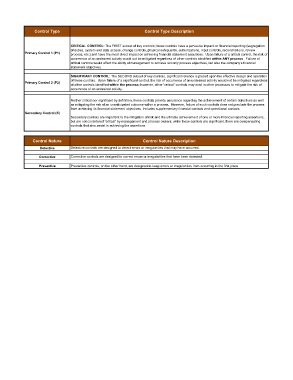
Control Type Control Type Description
CRITICAL CONTROL: The FIRST subset of key controls; these controls have a pervasive impact on financial reporting (segregation
of duties, system and data access, change controls, physical safeguards, authorizations, input controls, reconciliations, review
Primary Control 1 (P1) process, etc.) and have the most direct impact on achieving financial statement assertions. Upon failure of a critical control, the risk of
occurrence of an undesired activity would not be mitigated regardless of other controls identified within ANY process. Failure of
critical controls would affect the ability of management to achieve not only process objectives, but also the company’s financial
statement objectives.
SIGNIFICANT CONTROL: The SECOND subset of key controls, significant reliance is placed upon the effective design and operation
of these controls. Upon failure of a significant control, the risk of occurrence of an undesired activity would not be mitigated regardless
Primary Control 2 (P2)
of other controls identified within the process; however, other “critical” controls may exist in other processes to mitigate the risk of
occurrence of an undesired activity.
Neither critical nor significant by definition, these controls provide assurance regarding the achievement of certain objectives as well
as mitigating the risk of an unanticipated outcome within a process. However, failure of such controls does not preclude the process
from achieving its financial statement objectives. Includes supplementary financial controls and operational controls.
Secondary Control (S)
Secondary controls are important to the mitigation of risk and the ultimate achievement of one or more financial reporting assertions,
but are not considered “critical” by management and process owners; while these controls are significant, there are compensating
controls that also assist in achieving the assertions
Control Nature Control Nature Description
Detective Detective controls are designed to detect errors or irregularities that may have occurred.
Corrective Corrective controls are designed to correct errors or irregularities that have been detected.
Preventive Preventive controls, on the other hand, are designed to keep errors or irregularities from occurring in the first place.