Page 19 - Basics of Electrical, Electronic and Communication
P. 19
20 Chapter 2. Kirchoff’s laws
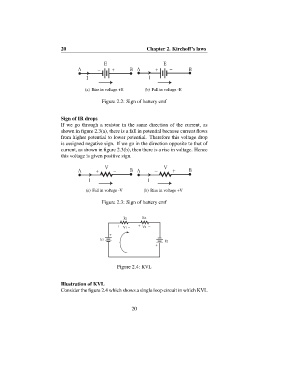
Ε Ε
Α − + Β Α + − Β
Ι Ι
(a) Rise in voltage +E (b) Fall in voltage -E
Figure 2.2: Sign of battery emf
Sign of IR drops
If we go through a resistor in the same direction of the current, as
shown in figure 2.3(a), there is a fall in potential because current flows
from higher potential to lower potential. Therefore this voltage drop
is assigned negative sign. If we go in the direction opposite to that of
current, as shown in figure 2.3(b), then there is a rise in voltage. Hence
this voltage is given positive sign.
V V
Α + − Β Α − + Β
I I
(a) Fall in voltage -V (b) Rise in voltage +V
Figure 2.3: Sign of battery emf
R1 R2
_ + _
+ V1 V2
+ _
E1
_ E2
+
Figure 2.4: KVL
Illustration of KVL
Consider the figure 2.4 which shows a single loop circuit in which KVL
20