Page 73 - The World About Us
P. 73
Glacial ice
1.1.1
1.1.1
2.2.3
2.3.1
How has climate changed in recent geological history?
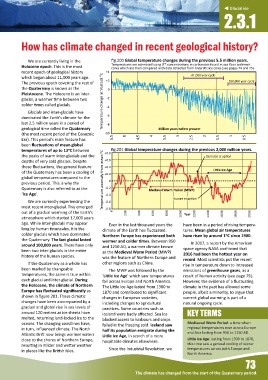
We are currently living in the fig.200 Global temperature changes during the previous 5.5 million years.
Temperatures are es mated using O¹⁸ concentra ons in carbonates found in sea floor sediment
Holocene epoch. This is the most cores which are then compared with data collected from Antarc c ice cores (see pages 74 and 75).
recent epoch of geological history +4 41,000 year cycle
which began about 11,000 years ago. 41,000 year cycle
100,000 year cycle
The previous epoch covering the rest of +2 100,000 year cycle
the Quaternary is known as the 0
Pleistocene. The Holocene is an inter-
glacial, a warmer me between two Temperature change at Vostock ⁰C -2 Temperature change at Vostock ⁰C
colder mes called glacials. -4
Glacials and inter-glacials have
dominated the Earth's climate for the -6
last 2.5 million years in a period of -8
geological me called the Quaternary Million years before present
(the most recent period of the Cenozoic -10 5 4 3 2 1
Era). This period’s main feature has 5.5 4.5 3.5 2.5 1.5 0.5
been fluctua ons of mean global
temperatures of up to 13 C between +0.8 fig.201 Global temperature changes during the previous 2,000 million years.
the peaks of warm inter-glacials and the Samalas erup on
depths of very cold glacials. Despite +0.6
these fluctua ons, the general feature +0.4
Li le Ice Agee
of the Quaternary has been a cooling of +0.2 Li le Ice Ag
global temperatures compared to the Temperature anomaly from mean ⁰C
previous period. This is why the 0
Quaternary is also referred to as the -0.2 Medieval Warm Period (MWP)
‘Ice Age’. -0.4
We are currently experiencing the -0.6 Kuwae erup on
most recent inter-glacial. This emerged -0.8
out of a gradual warming of the Earth's 0 200 400 600 800 1000 Year 1200 1400 1600 1800 2000
atmosphere which started 17,000 years
ago. While inter-glacials may appear Even in the last thousand years the have been in a period of rising tempera-
long by human mescales, it is the climate of the Earth has fluctuated. tures. Mean global air temperatures
colder glacials which have dominated Northern Europe has experienced both have risen by around 1 C since 1900.
the Quaternary. The last glacial lasted warmer and colder mes. Between 950
around 100,000 years. There have only and 1250 AD, a warmer climate known In 2017, a report by the American
been two inter-glacials in the en re as the Medieval Warm Period (MWP) space agency NASA confirmed that
history of the human species. was the feature of Northern Europe and 2016 had been the ho est year on
record. Most scien sts put the recent
If the Quaternary as a whole has other regions such as China. rise in temperature down to increased
been marked by changeable The MWP was followed by the emissions of greenhouse gases, as a
temperatures, the same is true within ‘Li le Ice Age’ which saw temperatures result of human ac vity (see page 79).
each glacial and inter-glacial. During fall across Europe and North America. However, the evidence of a fluctua ng
the Holocene, the climate of Northern The Li le Ice Age lasted from 1300 to climate in the past has allowed some
Europe has fluctuated significantly as 1870 and contributed to significant people, albeit a minority, to argue that
shown in figure 201. These clima c changes in European socie es, current global warming is part of a
changes have been accompanied by a including changes to agricultural natural ongoing cycle.
gradual and global rise in sea levels of prac ces. Some countries such as
around 120 metres as ice sheets have Iceland were badly affected. Sea ice KEY TERMS
melted, returning land-locked ice to the blocked access to harbours and crops
oceans. The changing coastlines have, failed in the freezing cold. Iceland saw Mediaeval Warm Period: a time when
in turn, influenced climate. The North half its popula on emigrate during the regional temperatures rose across Europe
Atlan c Dri now brings warmer waters Li le Ice Age, in search of a more and Asia lasting from 950 to 1250 AD.
close to the shores of Northern Europe, hospitable climates elsewhere. Little Ice Age: lasting from 1300 to 1870,
resul ng in milder and we er weather this time saw a general cooling of winter
in places like the Bri sh Isles. Since the Industrial Revolu on, we temperatures across both Europe and
North America.
73
The climate has changed from the start of the Quaternary period.