Page 11 - UNIT 3 - CONSTRUCTION OF FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT
P. 11
Civil Engineering Department | DCC3113 : Highway & Traffic Engineering
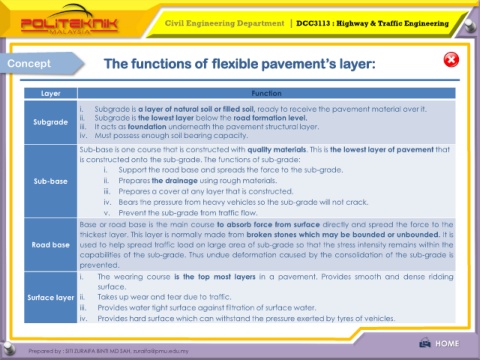
Concept The functions of flexible pavement’s layer:
Layer Function
i. Subgrade is a layer of natural soil or filled soil, ready to receive the pavement material over it.
ii. Subgrade is the lowest layer below the road formation level.
Subgrade
iii. It acts as foundation underneath the pavement structural layer.
iv. Must possess enough soil bearing capacity.
Sub-base is one course that is constructed with quality materials. This is the lowest layer of pavement that
is constructed onto the sub-grade. The functions of sub-grade:
i. Support the road base and spreads the force to the sub-grade.
Sub-base ii. Prepares the drainage using rough materials.
iii. Prepares a cover at any layer that is constructed.
iv. Bears the pressure from heavy vehicles so the sub-grade will not crack.
v. Prevent the sub-grade from traffic flow.
Base or road base is the main course to absorb force from surface directly and spread the force to the
thickest layer. This layer is normally made from broken stones which may be bounded or unbounded. It is
Road base used to help spread traffic load on large area of sub-grade so that the stress intensity remains within the
capabilities of the sub-grade. Thus undue deformation caused by the consolidation of the sub-grade is
prevented.
i. The wearing course is the top most layers in a pavement. Provides smooth and dense ridding
surface.
Surface layer ii. Takes up wear and tear due to traffic.
iii. Provides water tight surface against filtration of surface water.
iv. Provides hard surface which can withstand the pressure exerted by tyres of vehicles.
HOME
Prepared by : SITI ZURAIFA BINTI MD SAH, zuraifa@pmu.edu.my