Page 16 - Law Society of Hong Kong MPMC Manual v8 - With checklists (1 March 2018)
P. 16
Practice Management Course | Unit 2
Financial Management
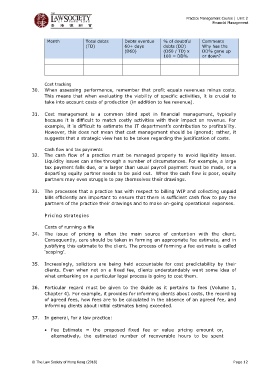
Month Total debts Debts overdue % of doubtful Comments
(TD) 60+ days debts (DD) Why has the
(D60) (D60 / TD) x DD% gone up
100 = DD% or down?
Cost tracking
30. When assessing performance, remember that profit equals revenues minus costs.
This means that when evaluating the viability of specific activities, it is crucial to
take into account costs of production (in addition to fee revenue).
31. Cost management is a common blind spot in financial management, typically
because it is difficult to match costly activities with their impact on revenue. For
example, it is difficult to estimate the IT department’s contribution to profitability.
However, this does not mean that cost management should be ignored; rather, it
suggests that a strategic view has to be taken regarding the justification of costs.
Cash flow and tax payments
32. The cash flow of a practice must be managed properly to avoid liquidity issues.
Liquidity issues can arise through a number of circumstances. For example, a large
tax payment falls due, or a larger than usual payroll payment must be made, or a
departing equity partner needs to be paid out. When the cash flow is poor, equity
partners may even struggle to pay themselves their drawings.
33. The processes that a practice has with respect to billing WIP and collecting unpaid
bills efficiently are important to ensure that there is sufficient cash flow to pay the
partners of the practice their drawings and to make on-going operational expenses.
Pricing strategies
Costs of running a file
34. The issue of pricing is often the main source of contention with the client.
Consequently, care should be taken in forming an appropriate fee estimate, and in
justifying this estimate to the client. The process of forming a fee estimate is called
‘scoping’.
35. Increasingly, solicitors are being held accountable for cost predictability by their
clients. Even when not on a fixed fee, clients understandably want some idea of
what embarking on a particular legal process is going to cost them.
36. Particular regard must be given to the Guide as it pertains to fees (Volume 1,
Chapter 4). For example, it provides for informing clients about costs, the recording
of agreed fees, how fees are to be calculated in the absence of an agreed fee, and
informing clients about initial estimates being exceeded.
37. In general, for a law practice:
• Fee Estimate = the proposed fixed fee or value pricing amount or,
alternatively, the estimated number of recoverable hours to be spent
© The Law Society of Hong Kong (2018) Page 12