Page 187 - Proceeding of Atrans Young Researcher's Forum 2019_Neat
P. 187
“Transportation for A Better Life:
Smart Mobility for Now and Then”
23 August 2019, Bangkok, Thailand
the discontinuance stage. Two hypotheses can be travel mode choice, it was found that subjective
derived as follows: norms can induce actions and habits . Future
33
research should explore these concepts and integrate
H4: Carpoolers and non-carpoolers with interest them into the proposed stages of the carpooling
show higher positive attitude towards cycle. Secondly, there might be some discontinued
carpooling than discontinued carpoolers and carpoolers who re-decide to carpool again. These
non-carpoolers without interest; participants might be at the restart stage. However,
H5: Carpoolers and non-carpoolers with interest as this manuscript focuses on the first loop of
show higher intention to perform carpooling carpooling behaviour, the restart stage might be an
than discontinued carpoolers and non- interest for future studies.
carpoolers without interest.
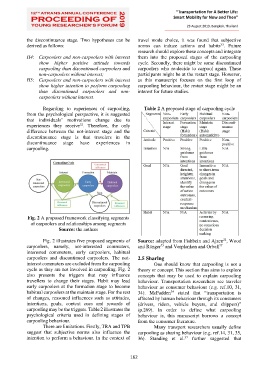
Regarding to experiences of carpooling, Table 2 A proposed stage of carpooling cycle
from the psychological perspective, it is suggested
that individuals’ motivations change due to
32
experiences they receive . Therefore, the only
difference between the not-interest stage and the
discontinuance stage is that travelers in the
discontinuance stage have experiences in
carpooling.
Fig. 2 A proposed framework classifying segments
of carpoolers and relationships among segments
Source: the authors
22
Fig. 2 illustrates five proposed segments of Source: adapted from Fishbein and Ajzen , Wood
carpoolers, namely, not-interested commuters, and Rünger and Verplanken and Orbell
25
27
interested commuters, early carpoolers, habitual
carpoolers and discontinued carpoolers. The not- 2.5 Sharing
interest commuters are excluded from the carpooling One should know that carpooling is not a
cycle as they are not involved in carpooling. Fig. 2 theory or concept. This section thus aims to explore
also presents the triggers that may influence concepts that may be used to explain carpooling
travellers to change their stages. Habit may lead behaviour. Transportation researchers see traveler
early carpoolers at the formation stage to become behaviour as consumer behaviour (e.g. ref.10, 31,
habitual carpoolers at the maintain stage. For the rest 34). McFadden stated that “transportation is
34
of changes, reasoned influences such as attitudes, affected by human behaviour through its consumers
intentions, goals, context cues and rewards of (drivers, riders, vehicle buyers, and shippers)”
carpooling may be the triggers. Table 2 illustrates the (p.269). In order to define what carpooling
psychological criteria used in defining stages of behaviour is, this manuscript borrows a concept
carpooling behaviour. from the consumer literature.
There are limitations. Firstly, TRA and TPB Many transport researchers usually define
suggest that subjective norms also influence the carpooling as sharing behaviour (e.g. ref.14, 31, 35,
intention to perform a behaviour. In the context of 36). Standing et al. further suggested that
37
162