Page 884 - Chief Architect Reference Manual
P. 884
Chief Architect X10 Reference Manual
• Blocking for standard and hip ridges gen- Truss. See “Drop Hip or California Hip”
erates as individual rafter objects between on page 889.
trusses.
• Lookouts will pass over Reduced Gable Manually Drawn Framing
trusses and will end at the next truss in. Unlike automatically generated roof framing,
See “Roof Truss Specification Dialog” on manually drawn rafters will extend through
page 892. trusses. Rafters can also snap to truss edges
• Hip ridges and common rafters at the end as they are being drawn or when they are
of a hip roof will pass over a Drop Hip being edited. See “Manual Framing” on page
838.
Truss Bases
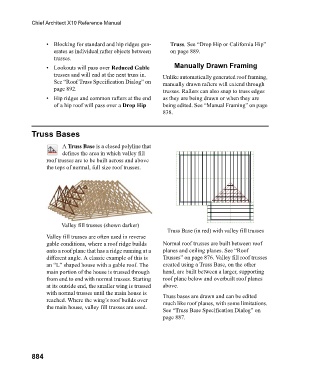
A Truss Base is a closed polyline that
defines the area in which valley fill
roof trusses are to be built across and above
the tops of normal, full size roof trusses.
Valley fill trusses (shown darker)
Truss Base (in red) with valley fill trusses
Valley fill trusses are often used in reverse
gable conditions, where a roof ridge builds Normal roof trusses are built between roof
onto a roof plane that has a ridge running at a planes and ceiling planes. See “Roof
different angle. A classic example of this is Trusses” on page 876. Valley fill roof trusses
an “L” shaped house with a gable roof. The created using a Truss Base, on the other
main portion of the house is trussed through hand, are built between a larger, supporting
from end to end with normal trusses. Starting roof plane below and overbuilt roof planes
at its outside end, the smaller wing is trussed above.
with normal trusses until the main house is Truss bases are drawn and can be edited
reached. Where the wing’s roof builds over much like roof planes, with some limitations.
the main house, valley fill trusses are used.
See “Truss Base Specification Dialog” on
page 887.
884