Page 9 - Laboratory manual for students FAR222 2019 20
P. 9
FAR 222 Dosage Form II Laboratory Manual
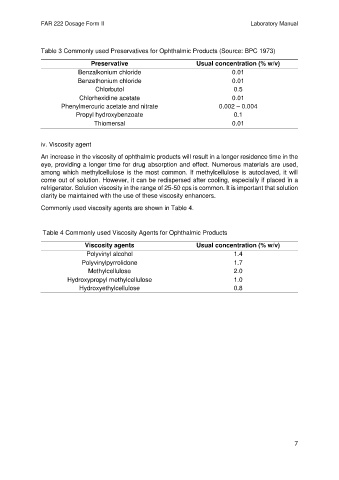
Table 3 Commonly used Preservatives for Ophthalmic Products (Source: BPC 1973)
Preservative Usual concentration (% w/v)
Benzalkonium chloride 0.01
Benzethonium chloride 0.01
Chlorbutol 0.5
Chlorhexidine acetate 0.01
Phenylmercuric acetate and nitrate 0.002 – 0.004
Propyl hydroxybenzoate 0.1
Thiomersal 0.01
iv. Viscosity agent
An increase in the viscosity of ophthalmic products will result in a longer residence time in the
eye, providing a longer time for drug absorption and effect. Numerous materials are used,
among which methylcellulose is the most common. If methylcellulose is autoclaved, it will
come out of solution. However, it can be redispersed after cooling, especially if placed in a
refrigerator. Solution viscosity in the range of 25-50 cps is common. It is important that solution
clarity be maintained with the use of these viscosity enhancers.
Commonly used viscosity agents are shown in Table 4.
Table 4 Commonly used Viscosity Agents for Ophthalmic Products
Viscosity agents Usual concentration (% w/v)
Polyvinyl alcohol 1.4
Polyvinylpyrrolidone 1.7
Methylcellulose 2.0
Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose 1.0
Hydroxyethylcellulose 0.8
7