Page 8 - Laboratory manual for students FAR222 2019 20
P. 8
FAR 222 Dosage Form II Laboratory Manual
adjustment is necessary if the patient is intolerant of pain and discomfort. Viscosity agent may
help to reduce some of the pain and discomfort if it is simply not possible to prepare the
solution within an acceptable range of tonicity. A hypotonic ophthalmic solution will require the
addition of a substance (tonicity adjusting agent) to attain the proper tonicity range.
ii. Buffers
The adjustment of pH in eye drops is important as eyes are sensitive to pH changes. Majority
of ophthalmic drugs are weak bases and buffering is needed to maintain the stability of the
drugs in the formulation. In most cases, the addition of buffer could help in adjusting the tonicity
of ophthalmic products.
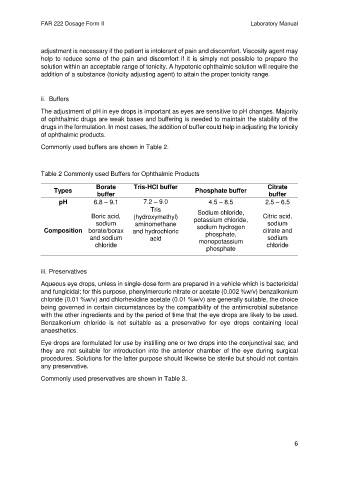
Commonly used buffers are shown in Table 2.
Table 2 Commonly used Buffers for Ophthalmic Products
Borate Tris-HCl buffer Citrate
Types Phosphate buffer
buffer buffer
pH 6.8 – 9.1 7.2 – 9.0 4.5 – 8.5 2.5 – 6.5
Tris
Sodium chloride,
Boric acid, (hydroxymethyl) potassium chloride, Citric acid,
sodium aminomethane sodium
Composition borate/borax and hydrochloric sodium hydrogen citrate and
phosphate,
and sodium acid monopotassium sodium
chloride chloride
phosphate
iii. Preservatives
Aqueous eye drops, unless in single-dose form are prepared in a vehicle which is bactericidal
and fungicidal; for this purpose, phenylmercuric nitrate or acetate (0.002 %w/v) benzalkonium
chloride (0.01 %w/v) and chlorhexidine acetate (0.01 %w/v) are generally suitable, the choice
being governed in certain circumstances by the compatibility of the antimicrobial substance
with the other ingredients and by the period of time that the eye drops are likely to be used.
Benzalkonium chloride is not suitable as a preservative for eye drops containing local
anaesthetics.
Eye drops are formulated for use by instilling one or two drops into the conjunctival sac, and
they are not suitable for introduction into the anterior chamber of the eye during surgical
procedures. Solutions for the latter purpose should likewise be sterile but should not contain
any preservative.
Commonly used preservatives are shown in Table 3.
6