Page 41 - demo
P. 41
PROCESS & TECHNOLOGY FOR METHANOL AND DME
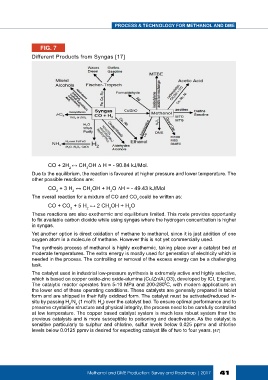
FIG. 7
Different Products from Syngas [17]
CO + 2H ↔ CH OH ∆ H = - 90.84 kJ/Mol.
2 3
Due to the equilibrium, the reaction is favoured at higher pressure and lower temperature. The
other possible reactions are:
CO + 3 H ↔ CH OH + H O ∆H = - 49.43 kJ/Mol
2 2 3 2
The overall reaction for a mixture of CO and CO could be written as:
2
CO + CO + 5 H ↔ 2 CH OH + H O
2 2 3 2
These reactions are also exothermic and equilibrium limited. This route provides opportunity
to fix available carbon dioxide while using syngas where the hydrogen concentration is higher
in syngas.
Yet another option is direct oxidation of methane to methanol, since it is just addition of one
oxygen atom in a molecule of methane. However this is not yet commercially used.
The synthesis process of methanol is highly exothermic, taking place over a catalyst bed at
moderate temperatures. The extra energy is mostly used for generation of electricity which is
needed in the process. The controlling or removal of the excess energy can be a challenging
task.
The catalyst used in industrial low-pressure synthesis is extremely active and highly selective,
which is based on copper oxide-zinc oxide-alumina (Cu/Zn/Al O3), developed by ICI, England.
2
The catalytic reactor operates from 5-10 MPa and 200-280 C, with modern applications on
0
the lower end of these operating conditions. These catalysts are generally prepared in tablet
form and are shipped in their fully oxidized form. The catalyst must be activated/reduced in-
situ by passing H /N (1 mol% H ) over the catalyst bed. To ensure optimal performance and to
2
2
2
preserve crystalline structure and physical integrity, the process need to be carefully controlled
at low temperature. The copper based catalyst system is much less robust system than the
previous catalysts and is more susceptible to poisoning and deactivation. As the catalyst is
sensitive particularly to sulphur and chlorine, sulfur levels below 0.025 ppmv and chlorine
levels below 0.0125 ppmv is desired for expecting catalyst life of two to four years. [47]
Methanol and DME Production: Survey and Roadmap | 2017 41