Page 63 - demo
P. 63
INDIAN SCENARIO
The non-combustible material in coal is returned as ash from a coal based furnace. There are
three different types of these by products, depending upon its characteristics. It contains arsenic,
mercury, lead, and several other heavy metals. Due to these contaminations adequate care
is necessary in safe handling and disposal of these materials. There are mainly three types of
ash as indicated below:
• Fly ash, a very fine, powdery material composed mostly of silica made from the burning of
finely ground coal in a boiler.
• Bottom ash, a coarse ash particle that is too large to be carried up into the smoke stacks
so it forms in the bottom of the coal furnace.
• Boiler slag, molten bottom ash from slag tap and cyclone type furnaces that turns into
pellets that have a smooth glassy appearance after it is cooled with water.
Indian coals from Odisha region indicate that the major components of the ash are Silica,
Alumina and Iron oxides while the lime content is low. As a result the fusion temperature is
generally high for Indian coal ash. The ash fusion temperature varies within 1150 to 1600 C.
0
The sulfur present in the coal is mostly organically bound, therefore not much is left in the ash.
A typical ash analysis is shown in Table 16.
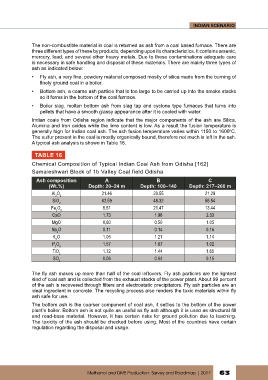
TABLE 16
Chemical Composition of Typical Indian Coal Ash from Odisha [162]
Samaleshwari Block of 1b Valley Coal field Odisha
Ash composition A B C
(Wt.%) Depth: 20–24 m Depth: 100–140 Depth: 217–260 m
Al O 3 21.46 20.55 21.29
2
SiO 2 62.59 48.32 56.54
Fe O 3 5.51 21.47 13.44
2
CaO 1.73 1.98 2.33
MgO 0,60 0.50 1.05
Na O 0.11 0.14 0.16
2
K O 1.05 1.21 1.14
2
P O 5 1.57 1.67 1.02
2
TiO 2 1.72 1.44 1.65
SO 0.06 0.04 0.15
3
The fly ash makes up more than half of the coal leftovers. Fly ash particles are the lightest
kind of coal ash and is collected from the exhaust stacks of the power plant. About 99 percent
of the ash is recovered through filters and electrostatic precipitators. Fly ash particles are an
ideal ingredient in concrete. The recycling process also renders the toxic materials within fly
ash safe for use.
The bottom ash is the coarser component of coal ash, it settles to the bottom of the power
plant’s boiler. Bottom ash is not quite as useful as fly ash although it is used as structural fill
and road-base material. However, it has certain risks for ground pollution due to leaching.
The toxicity of the ash should be checked before using. Most of the countries have certain
regulation regarding the disposal and usage.
Methanol and DME Production: Survey and Roadmap | 2017 63