Page 19 - A Canuck's Guide to Financial Literacy 2020
P. 19
19
Measurement of Risk
Standard Deviation
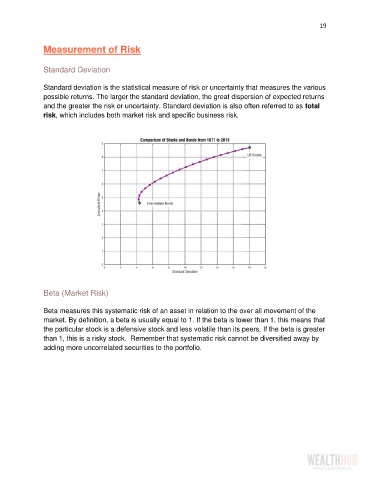
Standard deviation is the statistical measure of risk or uncertainty that measures the various
possible returns. The larger the standard deviation, the great dispersion of expected returns
and the greater the risk or uncertainty. Standard deviation is also often referred to as total
risk, which includes both market risk and specific business risk.
Beta (Market Risk)
Beta measures this systematic risk of an asset in relation to the over all movement of the
market. By definition, a beta is usually equal to 1. If the beta is lower than 1, this means that
the particular stock is a defensive stock and less volatile than its peers. If the beta is greater
than 1, this is a risky stock. Remember that systematic risk cannot be diversified away by
adding more uncorrelated securities to the portfolio.