Page 333 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 333
P1: FAW
BLUK007-07 BLUK007-Kendall May 25, 2005 18:18 Char Count= 0
Chapter 7: Disorders of the spinal cord 329
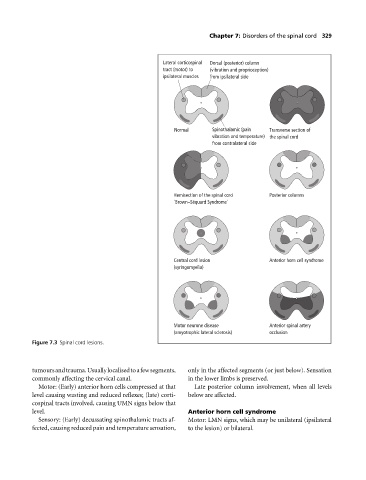
Lateral corticospinal Dorsal (posterior) column
tract (motor) to (vibration and proprioception)
ipsilateral muscles from ipsilateral side
Normal Spinothalamic (pain Transverse section of
vibration and temperature) the spinal cord
from contralateral side
Hemisection of the spinal cord Posterior columns
'Brown–Séquard Syndrome'
Central cord lesion Anterior horn cell syndrome
(syringomyelia)
Motor neurone disease Anterior spinal artery
(amyotrophic lateral sclerosis) occlusion
Figure 7.3 Spinal cord lesions.
tumoursandtrauma.Usuallylocalisedtoafewsegments, only in the affected segments (or just below). Sensation
commonly affecting the cervical canal. in the lower limbs is preserved.
Motor: (Early) anterior horn cells compressed at that Late posterior column involvement, when all levels
level causing wasting and reduced reflexes; (late) corti- below are affected.
cospinal tracts involved, causing UMN signs below that
level. Anterior horn cell syndrome
Sensory: (Early) decussating spinothalamic tracts af- Motor: LMN signs, which may be unilateral (ipsilateral
fected, causing reduced pain and temperature sensation, to the lesion) or bilateral.