Page 531 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 531
P1: KOA
BLUK007-15 BLUK007-Kendall May 12, 2005 20:54 Char Count= 0
Chapter 15: Overdose and poisoning 527
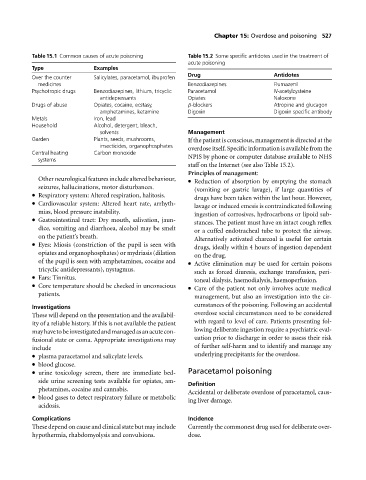
Table 15.1 Common causes of acute poisoning Table 15.2 Some specific antidotes used in the treatment of
acute poisoning
Type Examples
Drug Antidotes
Over the counter Salicylates, paracetamol, ibuprofen
medicines Benzodiazepines Flumazenil
Psychotropic drugs Benzodiazepines, lithium, tricyclic Paracetamol N-acetylcysteine
antidepressants Opiates Naloxone
Drugs of abuse Opiates, cocaine, ecstasy, β-blockers Atropine and glucagon
amphetamines, ketamine Digoxin Digoxin specific antibody
Metals Iron, lead
Household Alcohol, detergent, bleach,
solvents Management
Garden Plants, seeds, mushrooms, If the patient is conscious, management is directed at the
insecticides, organophosphates overdose itself. Specific information is available from the
Central heating Carbon monoxide
systems NPIS by phone or computer database available to NHS
staff on the Internet (see also Table 15.2).
Principles of management:
Other neurological features include altered behaviour, Reduction of absorption by emptying the stomach
seizures, hallucinations, motor disturbances.
(vomiting or gastric lavage), if large quantities of
Respiratory system: Altered respiration, halitosis.
drugs have been taken within the last hour. However,
Cardiovascular system: Altered heart rate, arrhyth-
lavage or induced emesis is contraindicated following
mias, blood pressure instability.
ingestion of corrosives, hydrocarbons or lipoid sub-
Gastrointestinal tract: Dry mouth, salivation, jaun-
stances. The patient must have an intact cough reflex
dice, vomiting and diarrhoea, alcohol may be smelt
or a cuffed endotracheal tube to protect the airway.
on the patient’s breath.
Alternatively activated charcoal is useful for certain
Eyes: Miosis (constriction of the pupil is seen with
drugs, ideally within 4 hours of ingestion dependent
opiates and organophosphates) or mydriasis (dilation
on the drug.
of the pupil is seen with amphetamines, cocaine and Active elimination may be used for certain poisons
tricyclic antidepressants), nystagmus.
such as forced diuresis, exchange transfusion, peri-
Ears: Tinnitus.
toneal dialysis, haemodialysis, haemoperfusion.
Core temperature should be checked in unconscious
Care of the patient not only involves acute medical
patients.
management, but also an investigation into the cir-
Investigations cumstances of the poisoning. Following an accidental
These will depend on the presentation and the availabil- overdose social circumstances need to be considered
ity of a reliable history. If this is not available the patient with regard to level of care. Patients presenting fol-
mayhavetobeinvestigatedandmanagedasanacutecon- lowing deliberate ingestion require a psychiatric eval-
fusional state or coma. Appropriate investigations may uation prior to discharge in order to assess their risk
include of further self-harm and to identify and manage any
plasma paracetamol and salicylate levels.
underlying precipitants for the overdose.
blood glucose.
urine toxicology screen, there are immediate bed-
Paracetamol poisoning
side urine screening tests available for opiates, am-
Definition
phetamines, cocaine and cannabis.
Accidental or deliberate overdose of paracetamol, caus-
blood gases to detect respiratory failure or metabolic
ing liver damage.
acidosis.
Complications Incidence
These depend on cause and clinical state but may include Currently the commonest drug used for deliberate over-
hypothermia, rhabdomyolysis and convulsions. dose.