Page 56 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 56
P1: JYS
BLUK007-02 BLUK007-Kendall May 25, 2005 17:25 Char Count= 0
52 Chapter 2: Cardiovascular system
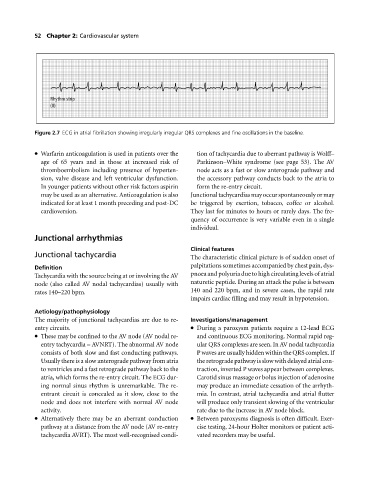
Rhythm strip
(II)
Figure 2.7 ECG in atrial fibrillation showing irregularly irregular QRS complexes and fine oscillations in the baseline.
Warfarin anticoagulation is used in patients over the tion of tachycardia due to aberrant pathway is Wolff–
age of 65 years and in those at increased risk of Parkinson–White syndrome (see page 53). The AV
thromboembolism including presence of hyperten- node acts as a fast or slow anterograde pathway and
sion, valve disease and left ventricular dysfunction. the accessory pathway conducts back to the atria to
In younger patients without other risk factors aspirin form the re-entry circuit.
may be used as an alternative. Anticoagulation is also Junctionaltachycardiasmayoccurspontaneouslyormay
indicated for at least 1 month preceding and post-DC be triggered by exertion, tobacco, coffee or alcohol.
cardioversion. They last for minutes to hours or rarely days. The fre-
quency of occurrence is very variable even in a single
individual.
Junctional arrhythmias
Clinical features
Junctional tachycardia The characteristic clinical picture is of sudden onset of
Definition palpitations sometimes accompanied by chest pain, dys-
Tachycardia with the source being at or involving the AV pnoea and polyuria due to high circulating levels of atrial
node (also called AV nodal tachycardias) usually with naturetic peptide. During an attack the pulse is between
rates 140–220 bpm. 140 and 220 bpm, and in severe cases, the rapid rate
impairs cardiac filling and may result in hypotension.
Aetiology/pathophysiology
The majority of junctional tachycardias are due to re- Investigations/management
entry circuits. During a paroxysm patients require a 12-lead ECG
These may be confined to the AV node (AV nodal re- and continuous ECG monitoring. Normal rapid reg-
entry tachycardia – AVNRT). The abnormal AV node ular QRS complexes are seen. In AV nodal tachycardia
consists of both slow and fast conducting pathways. Pwaves are usually hidden within the QRS complex. If
Usually there is a slow anterograde pathway from atria the retrograde pathway is slow with delayed atrial con-
to ventricles and a fast retrograde pathway back to the traction, inverted P waves appear between complexes.
atria, which forms the re-entry circuit. The ECG dur- Carotid sinus massage or bolus injection of adenosine
ing normal sinus rhythm is unremarkable. The re- may produce an immediate cessation of the arrhyth-
entrant circuit is concealed as it slow, close to the mia. In contrast, atrial tachycardia and atrial flutter
node and does not interfere with normal AV node will produce only transient slowing of the ventricular
activity. rate due to the increase in AV node block.
Alternatively there may be an aberrant conduction Between paroxysms diagnosis is often difficult. Exer-
pathway at a distance from the AV node (AV re-entry cise testing, 24-hour Holter monitors or patient acti-
tachycardia AVRT). The most well-recognised condi- vated recorders may be useful.