Page 62 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 62
P1: JYS
BLUK007-02 BLUK007-Kendall May 25, 2005 17:25 Char Count= 0
58 Chapter 2: Cardiovascular system
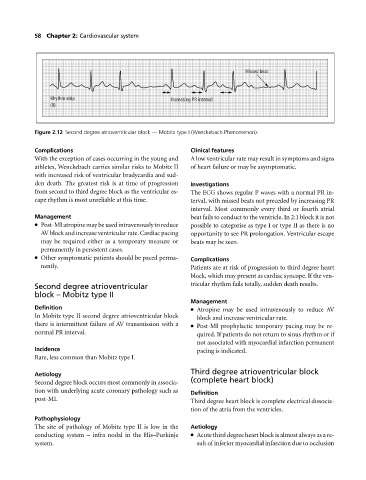
Missed beat
Rhythm strip Increasing PR interval
(II)
Figure 2.12 Second degree atrioventricular block — Mobitz type I (Wenckebach Phenomenon).
Complications Clinical features
With the exception of cases occurring in the young and Alow ventricular rate may result in symptoms and signs
athletes, Wenckebach carries similar risks to Mobitz II of heart failure or may be asymptomatic.
with increased risk of ventricular bradycardia and sud-
den death. The greatest risk is at time of progression Investigations
from second to third degree block as the ventricular es- The ECG shows regular P waves with a normal PR in-
cape rhythm is most unreliable at this time. terval, with missed beats not preceded by increasing PR
interval. Most commonly every third or fourth atrial
Management beat fails to conduct to the ventricle. In 2:1 block it is not
Post-MI atropine may be used intravenously to reduce possible to categorise as type I or type II as there is no
AV block and increase ventricular rate. Cardiac pacing opportunity to see PR prolongation. Ventricular escape
may be required either as a temporary measure or beats may be seen.
permanently in persistent cases.
Other symptomatic patients should be paced perma- Complications
nently. Patients are at risk of progression to third degree heart
block, which may present as cardiac syncope. If the ven-
Second degree atrioventricular tricular rhythm fails totally, sudden death results.
block – Mobitz type II
Management
Definition Atropine may be used intravenously to reduce AV
In Mobitz type II second degree atrioventricular block block and increase ventricular rate.
there is intermittent failure of AV transmission with a Post-MI prophylactic temporary pacing may be re-
normal PR interval. quired. If patients do not return to sinus rhythm or if
not associated with myocardial infarction permanent
Incidence pacing is indicated.
Rare, less common than Mobitz type I.
Third degree atrioventricular block
Aetiology
(complete heart block)
Second degree block occurs most commonly in associa-
tion with underlying acute coronary pathology such as Definition
post-MI. Third degree heart block is complete electrical dissocia-
tion of the atria from the ventricles.
Pathophysiology
The site of pathology of Mobitz type II is low in the Aetiology
conducting system – infra nodal in the His–Purkinje Acute third degree heart block is almost always as a re-
system. sult of inferior myocardial infarction due to occlusion