Page 263 - Crisis in Higher Education
P. 263
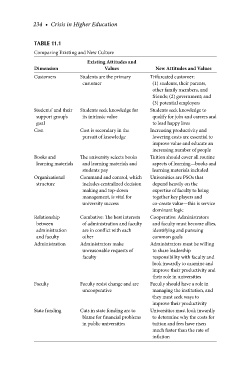
234 • Crisis in Higher Education
TABLE 11.1
Comparing Existing and New Culture
Existing Attitudes and
Dimension Values New Attitudes and Values
Customers Students are the primary Trifurcated customer:
customer (1) students, their parents,
other family members, and
friends; (2) government; and
(3) potential employers
Students’ and their Students seek knowledge for Students seek knowledge to
support group’s its intrinsic value qualify for jobs and careers and
goal to lead happy lives
Cost Cost is secondary in the Increasing productivity and
pursuit of knowledge lowering costs are essential to
improve value and educate an
increasing number of people
Books and The university selects books Tuition should cover all routine
learning materials and learning materials and aspects of learning—books and
students pay learning materials included
Organizational Command and control, which Universities are PSOs that
structure includes centralized decision depend heavily on the
making and top-down expertise of faculty to bring
management, is vital for together key players and
university success co-create value—this is service
dominant logic
Relationship Combative: The best interests Cooperative: Administrators
between of administration and faculty and faculty must become allies,
administration are in conflict with each identifying and pursuing
and faculty other common goals
Administration Administrators make Administrators must be willing
unreasonable requests of to share leadership
faculty responsibility with faculty and
look inwardly to examine and
improve their productivity and
their role in universities
Faculty Faculty resist change and are Faculty should have a role in
uncooperative managing the institution, and
they must seek ways to
improve their productivity
State funding Cuts in state funding are to Universities must look inwardly
blame for financial problems to determine why the costs for
in public universities tuition and fees have risen
much faster than the rate of
inflation