Page 7 - BBC Sky at Night Beginners Guide to Astronomy - 2017 UK
P. 7
❯ WHAT TO USE ❯ WHAT TO SEE
• Choosing telescopes and binoculars • Observing the Sun, Moon and planets
• Mounts, eyepieces and fi lters • Double stars, clusters and the Milky Way
• Get started in astrophotography • Nebulae and other deep-sky objects
GETTING USED TO THE DARK
In order to see the stars properly you need to take into account a very TOP TIPS
important factor to do with your eyes. This is called dark adaptation
1. BE PREPARED
The more you can
You’ll notice your pupils are set up before it gets
larger in dark conditions to let dark the better.
in more light, and smaller on a Leave items such as
bright sunny day so as not to maps and binoculars
dazzle you. This is actually only by the back door.
a small part of what your eyes
are up to. 2. KEEP WARM
Basically, eyes adapt to It can get quite chilly
whatever the lighting conditions outside, so take
are. Let’s take an example: a out or wear a coat,
room at night with the lights on. maybe a hat, and
It all looks fi ne because your some gloves.
Pp
eyes have set themselves to Pupils are smaller in ils are smaller in In the dark, your pupils grow Ith d k il 3. KEEP
work in whatever light there is bright conditions so that the bigger to let in more light – vital COMFORTABLE
around. Now turn the lights off light does not dazzle for seeing the stars Standing and
and the fi rst thing you’ll notice gazing up can be
is that the room appears almost begin to switch on the low-light- In other words, to see the a strain on the neck
black for a short time. Your intensity ‘rods’ which fi ll the best of the faint night sky, shield – using a deckchair
eyes, sensing the lack of light, backs of the eyes, so you can your eyes from bright lights for is a good solution.
have gone into dark-adapting see more. This process actually a good few minutes before you
mode – your pupils grow to takes around an hour, but a start stargazing. Plus, make sure 4. OBSERVING SITE
let in more light and then the good proportion is complete you cannot see any bright lights Check that where
all-important chemical changes within 10 minutes or so. while you are observing. you are observing
is free from holes,
dips, low walls or
anything you could
trip over in the dark.
5. DARK ADAPTATION
Give yourself a
good fi ve to 10
minutes (for starters)
for your eyes to get
used to the night sky
– you’ll see many
more stars.
6. RED TORCH
To preserve your
dark-adapted eyes,
only use a torch
covered with a red
plastic fi lter, or invest
in a dedicated red
light torch.
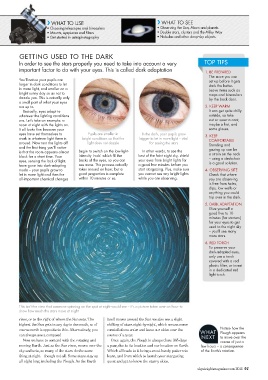
This isn’t the view that someone spinning on the spot at night would see – it’s a picture taken over an hour to
show how much the stars move at night
rises, or to the right of where the Sun sets. The itself moves around the Sun we also see a slight
highest the Sun gets in any day is due south, so of shifting of stars night-by-night, which means some
Notice how the
course north is opposite to this. Alternatively, you constellations enter and leave our skies over the WHAT
can always use a compass! course of a year. NEXT Plough appears
to move over the
Now we have to contend with the rotating and Once again, the Plough is always there 365 days course of just a
moving Earth. Just as the Sun rises, moves over the a year, due to its location and our location on Earth. few hours – a consequence
sky and sets, so many of the stars do the same Which all leads to it being a most handy pattern to of the Earth’s rotation.
thing at night – though not all. Some stars stay up learn, and from which to launch your stargazing
all night long, including the Plough. As the Earth quest and get to know the starry skies.
skyatnightmagazine.com 2012 07