Page 63 - Science
P. 63
RESEARCH
◥ foreign DNA invasion. The systems discovered
RESEARCH ARTICLE SUMMARY include ones that seem to have adopted com-
ponents of the bacterial flagella and chro-
mosome maintenance complexes and use these
MICROBIOLOGY
components for defensive capacities. Our data
also show that genes with Toll-interleukin re-
Systematic discovery of ceptor (TIR) domains are involved in bacte-
rial defense against phages, providing evidence
antiphage defense systems for a common, ancient ancestry of innate im-
munity components shared between animals,
in the microbial pangenome plants, and bacteria.
CONCLUSIONS: Our study expands the known
arsenal of defense systems used by prokaryotes
Shany Doron,* Sarah Melamed,* Gal Ofir, Azita Leavitt, Anna Lopatina,
Mai Keren, Gil Amitai, Rotem Sorek† for protection against phages, exposing tens of
thousands of instances of defense systems that
were so far unknown. Some of these systems
INTRODUCTION: Bacteria and archaea are antiphage defense. In this study, we aimed to appear to employ completely new mechanisms
frequently attacked by viruses (phages) and as comprehensively identify and experimentally ◥ of defense against phages.
a result have developed multiple, sophisticated verifynew defensesystems basedontheir en- ON OUR WEBSITE In the past, the discovery
lines of active defense that can collectively richment within defense islands in an attempt and mechanistic under-
Read the full article
be referred to as the prokaryotic “immune sys- to systematically map the arsenal of defense at http://dx.doi. standing of antiphage de-
tem.” Although bacterial defense against phages tools that are at the disposal of microbes in org/10.1126/ fense systems led to the
has been studied for decades, it was suggested their fight against phages. science.aar4120 development of important Downloaded from
..................................................
that many currently unknown defense systems biotechnological tools, as
reside in the genomes of nonmodel bacteria RESULTS: We searched for gene cassettes of exemplified by the use of restriction enzymes
and archaea and await discovery. unknown function that are enriched near and CRISPR-Cas for biotechnological and bio-
known defense systems in more than 45,000 medical applications. One may envision that
RATIONALE: Antiphage defense systems are available bacterial and archaeal genome se- some of the systems discovered in the current
known to be frequently physically clustered quences. Such gene cassettes were defined as study, once their mechanism is deciphered, will
in microbial genomes such that, for example, candidate defense systems and were system- also be adapted into useful molecular tools in
genes encoding restriction enzymes common- atically engineered into model bacteria, which the future. ▪ http://science.sciencemag.org/
ly reside in the vicinity of genes encoding other were then infected by an array of phages to
phage resistance systems. The observation that test for antiphage activities. This yielded the
defensesystems areclustered in genomic “de- discovery of nine new families of antiphage The list of author affiliations is available in the full article online.
fense islands” has led to the hypothesis that defense systems and one additional family of *These authors contributed equally to this work.
†Corresponding author. Email: rotem.sorek@weizmann.ac.il
genes of unknown function residing within antiplasmid systems that are widespread in Cite this article as S. Doron et al., Science 359,eaar4120
such defense islands may also participate in microbes and shown to strongly protect against (2018). DOI: 10.1126/science.aar4120 on March 1, 2018
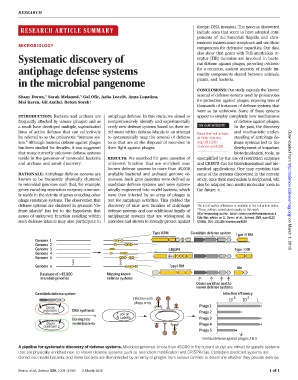
A pipeline for systematic discovery of defense systems. Microbial genomes (more than 45,000 in the current study) are mined for genetic systems
that are physically enriched next to known defense systems such as restriction-modification and CRISPR-Cas. Candidate predicted systems are
cloned into model bacteria, and these bacteria are then infected by an array of phages from various families to determine whether they provide defense.
Doron et al., Science 359, 1008 (2018) 2 March 2018 1of 1