Page 12 - p j 2018_Neat
P. 12
There are two types of polar climate: ET, or tundra climate; and EF, or ice cap climate. A tundra climate is characterized
by having at least one month whose average temperature is above 0 °C (32 °F), while an ice cap climate has no months
above 0 °C (32 °F).[2][clarification needed] In a tundra climate, trees cannot grow, but other specialized plants can grow.
In an ice cap climate, no plants can grow, and ice gradually accumulates until it flows elsewhere. Many high altitude
locations on Earth have a climate where no month has an average temperature of 10 °C (50 °F) or higher, but as this is due
to elevation, this climate is referred to as Alpine climate. Alpine climate can mimic either tundra or ice cap climate.
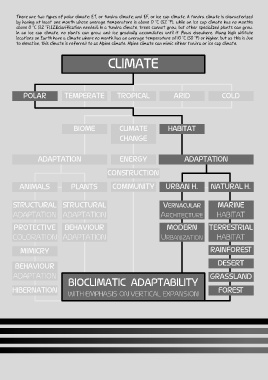
CLIMATE
POLAR TEMPERATE TROPICAL ARID COLD
BIOME CLIMATE HABITAT
CHANGE
ADAPTATION ENERGY ADAPTATION VERNACULAR ARCHITECTGURE
CON RUCTION
ANIMALS PLANTS COMMUNITY URBAN H. NATURAL H.
RUCTURAL RUCTURAL VERNACULAR MARINE
ADAPTATION ADAPTATION ARCHITECTURE HABITAT
PROTECTIVE BEHAVIOUR MODERN TERRE RIAL
COLORATION ADAPTATION URBANIZATION HABITAT
MIMICRY RAINFORE URBAN HABITAT
BEHAVIOUR DESERT
ADAPTATION GRASSLAND
BIOCLIMATIC ADAPTABILITY
HIBERNATION FORE
WITH EMPHASIS ON VERTICAL EXPANSION
GSPublisherVersion 0.7.100.100