Page 50 - VIRANSH COACHING CLASSES
P. 50
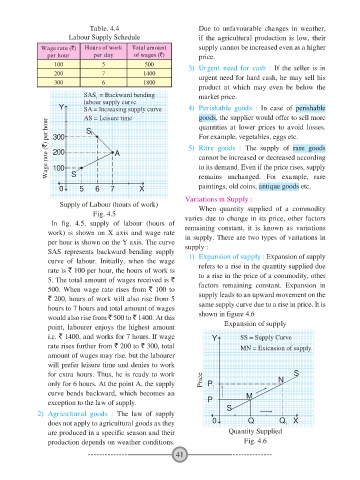
Table. 4.4 Due to unfavourable changes in weather,
Labour Supply Schedule if the agricultural production is low, their
Wage rate (`) Hours of work Total amount supply cannot be increased even at a higher
per hour per day of wages (`) price.
100 5 500 3) Urgent need for cash : If the seller is in
200 7 1400 urgent need for hard cash, he may sell his
300 6 1800
product at which may even be below the
SAS = Backward bending market price.
1
labour supply curve
Y SA = Increasing supply curve 4) Perishable goods : In case of perishable
AS = Leisure time goods, the supplier would offer to sell more
Wage rate (`) per hour 300 1 A 5) Rare goods : The supply of rare goods
quantities at lower prices to avoid losses.
S
For example, vegetables, eggs etc.
200
cannot be increased or decreased according
to its demand. Even if the price rises, supply
100
S
remains unchanged. For example, rare
paintings, old coins, antique goods etc.
0 5 6 7 X
Variations in Supply :
Supply of Labour (hours of work) When quantity supplied of a commodity
Fig. 4.5
In fig. 4.5, supply of labour (hours of varies due to change in its price, other factors
remaining constant, it is known as variations
work) is shown on X axis and wage rate in supply. There are two types of variations in
per hour is shown on the Y axis. The curve supply :
SAS represents backward bending supply
curve of labour. Initially, when the wage 1) Expansion of supply : Expansion of supply
rate is ` 100 per hour, the hours of work is refers to a rise in the quantity supplied due
to a rise in the price of a commodity, other
5. The total amount of wages received is `
500. When wage rate rises from ` 100 to factors remaining constant. Expansion in
` 200, hours of work will also rise from 5 supply leads to an upward movement on the
hours to 7 hours and total amount of wages same supply curve due to a rise in price. It is
would also rise from ` 500 to ` 1400. At this shown in figure 4.6
point, labourer enjoys the highest amount Expansion of supply
i.e. ` 1400, and works for 7 hours. If wage Y SS = Supply Curve
rate rises further from ` 200 to ` 300, total MN = Extension of supply
amount of wages may rise, but the labourer
will prefer leisure time and denies to work
for extra hours. Thus, he is ready to work S
only for 6 hours. At the point A, the supply Price P 1 N
curve bends backward, which becomes an M
exception to the law of supply. P
S
2) Agricultural goods : The law of supply
does not apply to agricultural goods as they 0 Q Q 1 X
are produced in a specific season and their Quantity Supplied
production depends on weather conditions. Fig. 4.6
41