Page 10 - 40163_Cardiology Overview Brochure modi 181217 copy
P. 10
Familial Hypercholesterolemia Testing
Familial hypercholesterolemia is an inherited cardiovascular disorder characterized by significantly elevated LDL cholesterol
levels. These significantly elevated LDL cholesterol levels can accelerate the development of plaques and atherosclerosis
in patients, and lead to a markedly increased risk of coronary artery disease at an early age. Up to 90% of FH cases are
undiagnosed.
Personal and Family History Red Flags
Coronary heart disease and/or heart attacks at an early History of xanthomas - Yellowish cholesterol buildup in
age particular areas of the body (especially eyes, skin, and
High LDL cholesterol levels: greater than 190 mg/dL in tendons)
adults or greater than 160 mg/dL in children History of arcus cornealis - White, gray, or blue opaque
ring in the corneal margin caused by cholesterol deposits
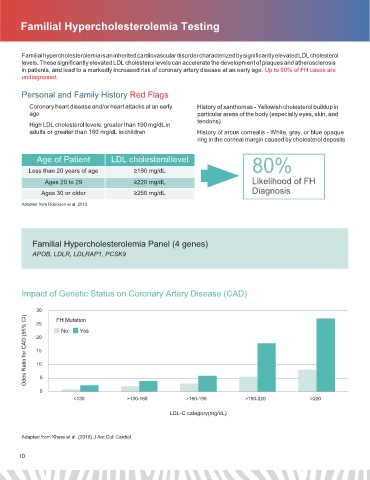
Age of Patient LDL cholesterol level 80%
Less than 20 years of age ≥190 mg/dL
Ages 20 to 29 ≥220 mg/dL Likelihood of FH
Ages 30 or older ≥250 mg/dL Diagnosis
Adapted from Robinson et al. 2013.
Familial Hypercholesterolemia Panel (4 genes)
APOB, LDLR, LDLRAP1, PCSK9
Impact of Genetic Status on Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
30 FH Mutation
Odds Ratio for CAD (95% CI) 20 No Yes
25
15
10
5
0
<130 >130-160 >160-190 >190-220 >220
LDL-C category(mg/dL)
Adapted from Khera et al. (2016) J Am Coll Cardiol.
10