Page 5 - 40163_Cardiology Overview Brochure modi 181217 copy
P. 5
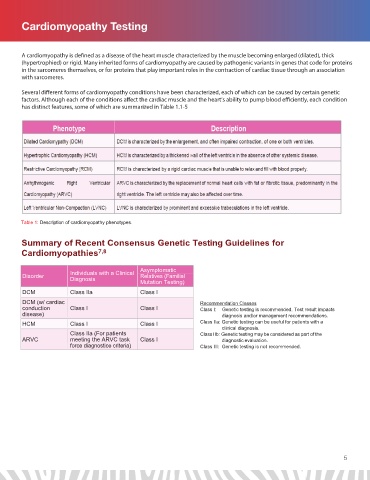
Cardiomyopathy Testing
A cardiomyopathy is de ned as a disease of the heart muscle characterized by the muscle becoming enlarged (dilated), thick
(hypertrophied) or rigid. Many inherited forms of cardiomyopathy are caused by pathogenic variants in genes that code for proteins
in the sarcomeres themselves, or for proteins that play important roles in the contraction of cardiac tissue through an association
with sarcomeres.
Several di erent forms of cardiomyopathy conditions have been characterized, each of which can be caused by certain genetic
factors. Although each of the conditions a ect the cardiac muscle and the heart’s ability to pump blood e ciently, each condition
has distinct features, some of which are summarized in Table 1.1-5
Table 1: Description of cardiomyopathy phenotypes.
Summary of Recent Consensus Genetic Testing Guidelines for
Cardiomyopathies 7,8
Relatives (Familial
Disorder Individuals with a Clinical Asymptomatic
Diagnosis
Mutation Testing)
DCM Class IIa Class I
DCM (w/ cardiac Recommendation Classes
conduction Class I Class I Class I: Genetic testing is recommended. Test result impacts
disease) diagnosis and/or management recommendations.
HCM Class I Class I Class IIa: Genetic testing can be useful for patients with a
clinical diagnosis.
Class IIa (For patients Class IIb: Genetic testing may be considered as part of the
ARVC meeting the ARVC task Class I diagnostic evaluation.
force diagnostice criteria) Class III: Genetic testing is not recommended.
5