Page 5 - The Care and Handling of Flexible Scopes v3
P. 5
Care of Flexible Endoscopes
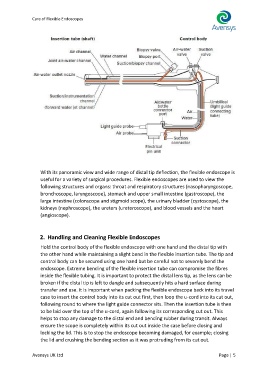
With its panoramic view and wide range of distal tip deflection, the flexible endoscope is
useful for a variety of surgical procedures. Flexible endoscopes are used to view the
following structures and organs: throat and respiratory structures (nasopharyngoscope,
bronchoscope, laryngoscope), stomach and upper small intestine (gastroscope), the
large intestine (colonscope and stigmoid scope), the urinary bladder (cystoscope), the
kidneys (nephroscope), the ureters (ureteroscope), and blood vessels and the heart
(angioscope).
2. Handling and Cleaning Flexible Endoscopes
Hold the control body of the flexible endoscope with one hand and the distal tip with
the other hand while maintaining a slight bend in the flexible insertion tube. The tip and
control body can be secured using one hand but be careful not to severely bend the
endoscope. Extreme bending of the flexible insertion tube can compromise the fibres
inside the flexible tubing. It is important to protect the distal lens tip, as the lens can be
broken if the distal tip is left to dangle and subsequently hits a hard surface during
transfer and use. It is important when packing the flexible endoscope back into its travel
case to insert the control body into its cut out first, then loop the u-cord into its cut out,
following round to where the light guide connector sits. Then the insertion tube is then
to be laid over the top of the u-cord, again following its corresponding cut out. This
helps to stop any damage to the distal end and bending rubber during transit. Always
ensure the scope is completely within its cut out inside the case before closing and
locking the lid. This is to stop the endoscope becoming damaged, for example; closing
the lid and crushing the bending section as it was protruding from its cut out.
Avensys UK Ltd Page | 5