Page 18 - PR 2014 2016 10 Materials and Nanotechnology
P. 18
294 Materials and Nanotechnology | Progress Report
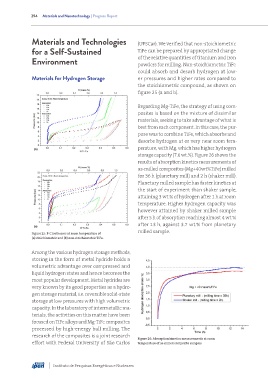
Materials and Technologies (UFSCar). We verified that non-stoichiometric
for a Self-Sustained TiFe can be prepared by appropriated change
Environment of the relative quantities of titanium and iron
powders for milling. Non-stoichiometric TiFe
could absorb and desorb hydrogen at low-
Materials for Hydrogen Storage er pressures and higher rates compared to
the stoichiometric compound, as shown on
figure 25 (a and b).
Regarding Mg-TiFe, the strategy of using com-
posites is based on the mixture of dissimilar
materials, seeking to take advantage of what is
best from each component. In this case, the pur-
pose was to combine TiFe, which absorbs and
desorbs hydrogen at or very near room tem-
perature, with Mg, which has higher hydrogen
storage capacity (7.6 wt.%). Figure 26 shows the
results of absorption kinetics measurements of
as-milled composites (Mg+40wt%TiFe) milled
for 36 h (planetary mill) and 2 h (shaker mill).
Planetary milled sample has faster kinetics at
the start of experiment than shaker sample,
attaining 3 wt.% of hydrogen after 1 h at room
temperature. Higher hydrogen capacity was
however attained by shaker milled sample
after 5 h of absorption reaching almost 4 wt.%
after 13 h, against 3.7 wt.% from planetary
milled sample.
Figure 25: P-C isotherms at room temperature of
(a) stoichiometric and (b) non-stoichiometric TiFe.
Among the various hydrogen storage methods,
storing in the form of metal hydride holds a
volumetric advantage over compressed and
liquid hydrogen states and hence becomes the
most popular development. Metal hydrides are
very known by its good properties as a hydro-
gen storage material, i.e. reversible solid-state
storage at low pressures with high volumetric
capacity. In the laboratory of intermetallic ma-
terials, the activities on this matter have been
focused on TiFe alloys and Mg-TiFe composites
processed by high-energy ball milling. The
research of the composites is a joint research
Figure 26: Absorption kinetics measurements at room
effort with Federal University of São Carlos temperature of as-milled composite samples
Instituto de Pesquisas Energéticas e Nucleares