Page 1292 - Equine Clinical Medicine, Surgery and Reproduction, 2nd Edition
P. 1292
Skin 1267
VetBooks.ir FIBROMA/FIBROSARCOMA Prognosis
The prognosis is generally good for fibroma, but
Definition/overview
The lesions are often single. They may be firm or soft, guarded for fibrosarcoma.
well-circumscribed, dermal or subcutaneous nodules, HAEMANGIOMA/
which may ulcerate or develop into a flattened verru- HAEMANGIOSARCOMA
cous lesion. Fibromas are benign. Fibrosarcomas may
be multiple and are locally invasive. Definition/overview
These are uncommon tumours of the vascular
Aetiology/pathophysiology system.
These are uncommon tumours in the horse, arising
from dermal or subcutaneous fibroblasts. They usu- Aetiology/pathophysiology
ally occur in older horses. They are benign or malignant neoplasms arising
from the endothelial cells of blood vessels.
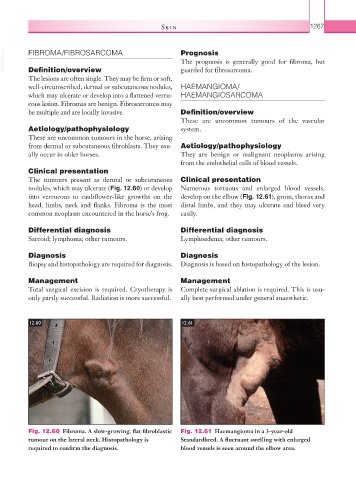
Clinical presentation
The tumours present as dermal or subcutaneous Clinical presentation
nodules, which may ulcerate (Fig. 12.60) or develop Numerous tortuous and enlarged blood vessels,
into verrucous to cauliflower-like growths on the develop on the elbow (Fig. 12.61), groin, thorax and
head, limbs, neck and flanks. Fibroma is the most distal limbs, and they may ulcerate and bleed very
common neoplasm encountered in the horse’s frog. easily.
Differential diagnosis Differential diagnosis
Sarcoid; lymphoma; other tumours. Lymphoedema; other tumours.
Diagnosis Diagnosis
Biopsy and histopathology are required for diagnosis. Diagnosis is based on histopathology of the lesion.
Management Management
Total surgical excision is required. Cryotherapy is Complete surgical ablation is required. This is usu-
only partly successful. Radiation is more successful. ally best performed under general anaesthetic.
12.60 12.61
Fig. 12.60 Fibroma. A slow-growing, flat fibroblastic Fig. 12.61 Haemangioma in a 3-year-old
tumour on the lateral neck. Histopathology is Standardbred. A fluctuant swelling with enlarged
required to confirm the diagnosis. blood vessels is seen around the elbow area.