Page 530 - Equine Clinical Medicine, Surgery and Reproduction, 2nd Edition
P. 530
Reproductive system: 2.1 The female reproductive tr act 505
VetBooks.ir 2.116 the cervix may be affected by adhesions, which will
require treatment. Uterine lavage and drainage over
a prolonged period may be required, along with spe-
cific antimicrobial intrauterine therapy. There is
risk of recurrence, and in such cases surgical ovar-
iohysterectomy can be considered in a two-stage
procedure (a standing flank laparoscopic approach
followed by a midline laparotomy under general
anaesthesia). The procedure is difficult, with a risk
of complications, most notably stump infection.
Prognosis
For future breeding the prognosis is poor, especially
if cervical or uterine adhesions are present or there
is recurrence of fluid accumulation. If there are
severe, deep, chronic inflammatory changes or end-
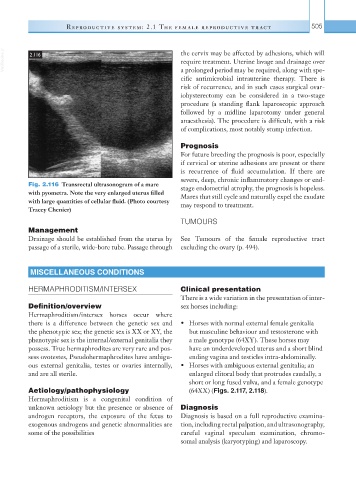
Fig. 2.116 Transrectal ultrasonogram of a mare stage endometrial atrophy, the prognosis is hopeless.
with pyometra. Note the very enlarged uterus filled Mares that still cycle and naturally expel the exudate
with large quantities of cellular fluid. (Photo courtesy may respond to treatment.
Tracey Chenier)
TUMOURS
Management
Drainage should be established from the uterus by See Tumours of the female reproductive tract
passage of a sterile, wide-bore tube. Passage through excluding the ovary (p. 494).
MISCELLANEOUS CONDITIONS
HERMAPHRODITISM/INTERSEX Clinical presentation
There is a wide variation in the presentation of inter-
Definition/overview sex horses including:
Hermaphroditism/intersex horses occur where
there is a difference between the genetic sex and • Horses with normal external female genitalia
the phenotypic sex; the genetic sex is XX or XY, the but masculine behaviour and testosterone with
phenotypic sex is the internal/external genitalia they a male genotype (64XY). These horses may
possess. True hermaphrodites are very rare and pos- have an underdeveloped uterus and a short blind
sess ovotestes, Pseudohermaphrodites have ambigu- ending vagina and testicles intra-abdominally.
ous external genitalia, testes or ovaries internally, • Horses with ambiguous external genitalia; an
and are all sterile. enlarged clitoral body that protrudes caudally, a
short or long fused vulva, and a female genotype
Aetiology/pathophysiology (64XX) (Figs. 2.117, 2.118).
Hermaphroditism is a congenital condition of
unknown aetiology but the presence or absence of Diagnosis
androgen receptors, the exposure of the fetus to Diagnosis is based on a full reproductive examina-
exogenous androgens and genetic abnormalities are tion, including rectal palpation, and ultrasonography,
some of the possibilities careful vaginal speculum examination, chromo-
somal analysis (karyotyping) and laparoscopy.