Page 531 - Equine Clinical Medicine, Surgery and Reproduction, 2nd Edition
P. 531
506 CHAPTER 2
VetBooks.ir 2.117 2.118
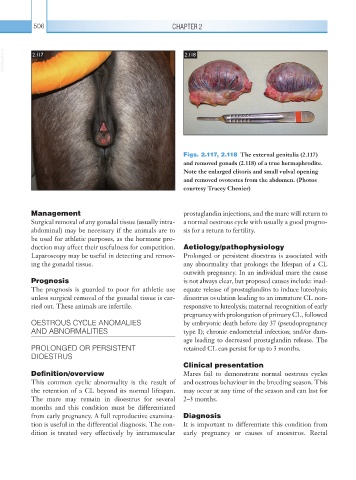
Figs. 2.117, 2.118 The external genitalia (2.117)
and removed gonads (2.118) of a true hermaphrodite.
Note the enlarged clitoris and small vulval opening
and removed ovotestes from the abdomen. (Photos
courtesy Tracey Chenier)
Management prostaglandin injections, and the mare will return to
Surgical removal of any gonadal tissue (usually intra- a normal oestrous cycle with usually a good progno-
abdominal) may be necessary if the animals are to sis for a return to fertility.
be used for athletic purposes, as the hormone pro-
duction may affect their usefulness for competition. Aetiology/pathophysiology
Laparoscopy may be useful in detecting and remov- Prolonged or persistent dioestrus is associated with
ing the gonadal tissue. any abnormality that prolongs the lifespan of a CL
outwith pregnancy. In an individual mare the cause
Prognosis is not always clear, but proposed causes include: inad-
The prognosis is guarded to poor for athletic use equate release of prostaglandins to induce luteolysis;
unless surgical removal of the gonadal tissue is car- dioestrus ovulation leading to an immature CL non-
ried out. These animals are infertile. responsive to luteolysis; maternal recognition of early
pregnancy with prolongation of primary CL, followed
OESTROUS CYCLE ANOMALIES by embryonic death before day 37 (pseudopregnancy
AND ABNORMALITIES type I); chronic endometrial infection; and/or dam-
age leading to decreased prostaglandin release. The
PROLONGED OR PERSISTENT retained CL can persist for up to 3 months.
DIOESTRUS
Clinical presentation
Definition/overview Mares fail to demonstrate normal oestrous cycles
This common cyclic abnormality is the result of and oestrous behaviour in the breeding season. This
the retention of a CL beyond its normal lifespan. may occur at any time of the season and can last for
The mare may remain in dioestrus for several 2–3 months.
months and this condition must be differentiated
from early pregnancy. A full reproductive examina- Diagnosis
tion is useful in the differential diagnosis. The con- It is important to differentiate this condition from
dition is treated very effectively by intramuscular early pregnancy or causes of anoestrus. Rectal