Page 617 - Equine Clinical Medicine, Surgery and Reproduction, 2nd Edition
P. 617
592 CHAPTER 3
VetBooks.ir areas of hyporesonance indicating absence of air- of the URT and the proximal trachea, but they are
too short for examination beyond the carina. Longer
filled lung (i.e. pleural fluid and/or consolidated
lung). Percussion is remarkably accurate for iden-
bronchial tree. Lengths between 2.4 and 3 metres
tifying pleural fluid lines. Occasionally, hyperreso- instruments are required for examination of the
nance may occur in recurrent airway obstruction are needed for collection of bronchoalveolar lavage
(RAO) cases due to lung hyperinflation. (BAL) samples.
As for clinical examination, a standard routine
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS should be used for endoscopic examination:
Respiratory endoscopy • Both sides of the nasal cavity: include the ventral
Respiratory endoscopy is a simple, well-tolerated and middle meati (to check for discharge from
and extremely informative investigation for both the region of the nasomaxillary openings).
the URT and the LRT. Most endoscopic examina- • Nasopharynx and soft palate (Fig. 3.3).
tions are facilitated by sedation to reduce coughing, • Guttural pouches: entry to the pouches
increase patient compliance and reduce the risk of requires an implement (either a closed biopsy
damage to patient and instrument; however, mean- forceps [Fig. 3.4] or, better, a solid, semi-rigid
ingful assessment of pharyngeal and laryngeal func- plastic introducing device inserted via the
tion can only be carried out in unsedated horses endoscope’s biopsy channel) to lever open the
because sedation causes relaxation of the naso- nasopharyngeal ostium of the pouch and allow
pharynx, flaccidity of the soft palate and decreased entry of the endoscope.
arytenoid abduction. Endoscopy allows direct exam- • Larynx: the resting position, movement and
ination of most of the tract and can be used to collect symmetry of the epiglottis, aryepiglottic folds,
lavage and biopsy samples. 1.0–1.5 metre × 8–12 mm arytenoids, vestibular folds, vocal folds and
fibreoptic video endoscopes are standard equipment lateral ventricle should be sssessed. Observe
in equine practices and are suitable for examination during and after swallowing for transient
3.3 3.4
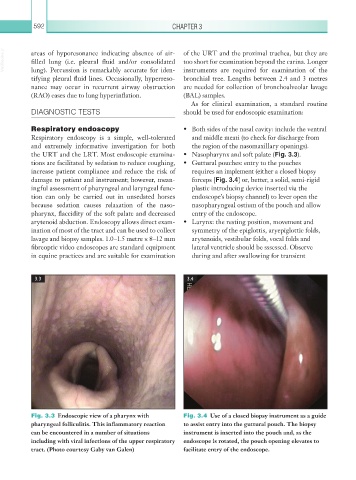
Fig. 3.3 Endoscopic view of a pharynx with Fig. 3.4 Use of a closed biopsy instrument as a guide
pharyngeal folliculitis. This inflammatory reaction to assist entry into the guttural pouch. The biopsy
can be encountered in a number of situations instrument is inserted into the pouch and, as the
including with viral infections of the upper respiratory endoscope is rotated, the pouch opening elevates to
tract. (Photo courtesy Gaby van Galen) facilitate entry of the endoscope.