Page 676 - Equine Clinical Medicine, Surgery and Reproduction, 2nd Edition
P. 676
Respir atory system: 3.2 Surgical conditions of the respir atory tr act 651
VetBooks.ir or where there are no concurrent abnormalities. Differential diagnosis
The differential diagnoses include all other causes of
This is ideally performed by transendoscopic laser
ablation of the folds, using traction on the fold
tion. Epiglottic hypoplasia is a similarly controversial
with broncho-esophageal forceps passed via the DDSP and many other causes of upper airway obstruc-
contralateral nostril. Resection can be performed condition that is a principal differential diagnosis.
via a laryngotomy incision although the precise
orientation of the fold can be harder to decide in Diagnosis
recumbency. Postoperatively, topical antibiotic and The diagnosis is established by endoscopic exami-
anti-inflammatory pharyngeal sprays may also nation in the non-sedated horse, and the observer’s
be used. Coughing and dysphagia do not appear opinion of the appearance of the epiglottis. This is
to be serious complications of this procedure, complicated by the fact that the epiglottis faces the
despite being recognised complications of sub- observer, making assessment of length difficult, and
epiglottic resection for the treatment of epiglottic can be isolated in space, making assessment of tex-
entrapment. ture difficult. A flaccid epiglottis is generally con-
sidered to be one which is flattened against the soft
Prognosis palate throughout its length, with the edges curl-
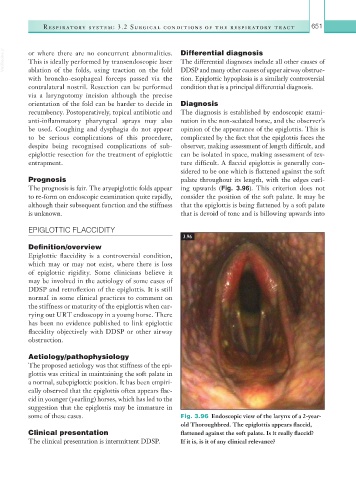
The prognosis is fair. The aryepiglottic folds appear ing upwards (Fig. 3.96). This criterion does not
to re-form on endoscopic examination quite rapidly, consider the position of the soft palate. It may be
although their subsequent function and the stiffness that the epiglottis is being flattened by a soft palate
is unknown. that is devoid of tone and is billowing upwards into
EPIGLOTTIC FLACCIDITY
3.96
Definition/overview
Epiglottic flaccidity is a controversial condition,
which may or may not exist, where there is loss
of epiglottic rigidity. Some clinicians believe it
may be involved in the aetiology of some cases of
DDSP and retroflexion of the epiglottis. It is still
normal in some clinical practices to comment on
the stiffness or maturity of the epiglottis when car-
rying out URT endoscopy in a young horse. There
has been no evidence published to link epiglottic
flaccidity objectively with DDSP or other airway
obstruction.
Aetiology/pathophysiology
The proposed aetiology was that stiffness of the epi-
glottis was critical in maintaining the soft palate in
a normal, subepiglottic position. It has been empiri-
cally observed that the epiglottis often appears flac-
cid in younger (yearling) horses, which has led to the
suggestion that the epiglottis may be immature in
some of these cases. Fig. 3.96 Endoscopic view of the larynx of a 2-year-
old Thoroughbred. The epiglottis appears flaccid,
Clinical presentation flattened against the soft palate. Is it really flaccid?
The clinical presentation is intermittent DDSP. If it is, is it of any clinical relevance?