Page 762 - Equine Clinical Medicine, Surgery and Reproduction, 2nd Edition
P. 762
Gastrointestinal system: 4.1 The upper gastrointestinal tr act 737
VetBooks.ir the soft tissues, followed by realignment and immo- 4.32
bilisation with external fixators, and intramedullary
pins (ostectomy) has been reported. Many neonates
are euthanased when the deformity is identified.
HETEROTROPIC POLYDONTIA
(DENTIGEROUS CYTS)
Definition /overview
Dentigerous cysts are anatomically inappropriate
dental tissue.
Aetiology/pathophysiology
Heterotropic polydontia is a well-recognised lesion
involving the presence of ectopic dental tissue con-
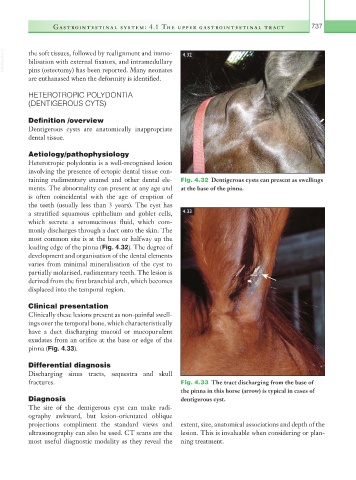
taining rudimentary enamel and other dental ele- Fig. 4.32 Dentigerous cysts can present as swellings
ments. The abnormality can present at any age and at the base of the pinna.
is often coincidental with the age of eruption of
the teeth (usually less than 3 years). The cyst has
a stratified squamous epithelium and goblet cells, 4.33
which secrete a seromucinous fluid, which com-
monly discharges through a duct onto the skin. The
most common site is at the base or halfway up the
leading edge of the pinna (Fig. 4.32). The degree of
development and organisation of the dental elements
varies from minimal mineralisation of the cyst to
partially molarised, rudimentary teeth. The lesion is
derived from the first branchial arch, which becomes
displaced into the temporal region.
Clinical presentation
Clinically these lesions present as non-painful swell-
ings over the temporal bone, which characteristically
have a duct discharging mucoid or mucopurulent
exudates from an orifice at the base or edge of the
pinna (Fig. 4.33).
Differential diagnosis
Discharging sinus tracts, sequestra and skull
fractures. Fig. 4.33 The tract discharging from the base of
the pinna in this horse (arrow) is typical in cases of
Diagnosis dentigerous cyst.
The site of the dentigerous cyst can make radi-
ography awkward, but lesion-orientated oblique
projections compliment the standard views and extent, size, anatomical associations and depth of the
ultrasonography can also be used. CT scans are the lesion. This is invaluable when considering or plan-
most useful diagnostic modality as they reveal the ning treatment.