Page 379 - Adams and Stashak's Lameness in Horses, 7th Edition
P. 379
Diagnostic Imaging 345
VetBooks.ir
A
B
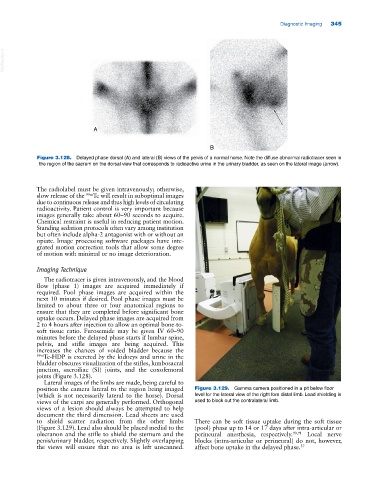
Figure 3.128. Delayed phase dorsal (A) and lateral (B) views of the pelvis of a normal horse. Note the diffuse abnormal radiotracer seen in
the region of the sacrum on the dorsal view that corresponds to radioactive urine in the urinary bladder, as seen on the lateral image (arrow).
The radiolabel must be given intravenously; otherwise,
slow release of the 99m Tc will result in suboptimal images
due to continuous release and thus high levels of circulating
radioactivity. Patient control is very important because
images generally take about 60–90 seconds to acquire.
Chemical restraint is useful in reducing patient motion.
Standing sedation protocols often vary among institution
but often include alpha‐2 antagonist with or without an
opiate. Image processing software packages have inte
grated motion correction tools that allow some degree
of motion with minimal or no image deterioration.
Imaging Technique
The radiotracer is given intravenously, and the blood
flow (phase 1) images are acquired immediately if
required. Pool phase images are acquired within the
next 10 minutes if desired. Pool phase images must be
limited to about three or four anatomical regions to
ensure that they are completed before significant bone
uptake occurs. Delayed phase images are acquired from
2 to 4 hours after injection to allow an optimal bone‐to‐
soft tissue ratio. Furosemide may be given IV 60–90
minutes before the delayed phase starts if lumbar spine,
pelvis, and stifle images are being acquired. This
increases the chances of voided bladder because the
99m Tc‐HDP is excreted by the kidneys and urine in the
bladder obscures visualization of the stifles, lumbosacral
junction, sacroiliac (SI) joints, and the coxofemoral
joints (Figure 3.128).
Lateral images of the limbs are made, being careful to
position the camera lateral to the region being imaged Figure 3.129. Gamma camera positioned in a pit below floor
(which is not necessarily lateral to the horse). Dorsal level for the lateral view of the right fore distal limb. Lead shielding is
views of the carpi are generally performed. Orthogonal used to block out the contralateral limb.
views of a lesion should always be attempted to help
document the third dimension. Lead sheets are used
to shield scatter radiation from the other limbs There can be soft tissue uptake during the soft tissue
(Figure 3.129). Lead also should be placed medial to the (pool) phase up to 14 or 17 days after intra‐articular or
olecranon and the stifle to shield the sternum and the perineural anesthesia, respectively. 90,91 Local nerve
penis/urinary bladder, respectively. Slightly overlapping blocks (intra‐articular or perineural) do not, however,
the views will ensure that no area is left unscanned. affect bone uptake in the delayed phase. 37