Page 529 - Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Disorders in Small Animal Practice
P. 529
Fluid and Diuretic Therapy in Heart Failure 517
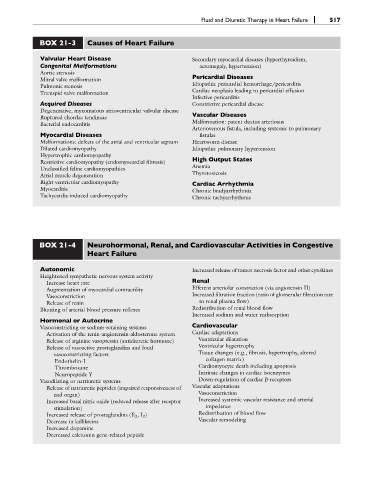
BOX 21-3 Causes of Heart Failure
Valvular Heart Disease Secondary myocardial diseases (hyperthyroidism,
Congenital Malformations acromegaly, hypertension)
Aortic stenosis Pericardial Diseases
Mitral valve malformation
Pulmonic stenosis Idiopathic pericardial hemorrhage/pericarditis
Tricuspid valve malformation Cardiac neoplasia leading to pericardial effusion
Infective pericarditis
Acquired Diseases Constrictive pericardial disease
Degenerative, myxomatous atrioventricular valvular disease Vascular Diseases
Ruptured chordae tendineae
Malformation: patent ductus arteriosus
Bacterial endocarditis
Arteriovenous fistula, including systemic to pulmonary
Myocardial Diseases fistulas
Malformations: defects of the atrial and ventricular septum Heartworm disease
Dilated cardiomyopathy Idiopathic pulmonary hypertension
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy High Output States
Restrictive cardiomyopathy (endomyocardial fibrosis)
Anemia
Unclassified feline cardiomyopathies
Thyrotoxicosis
Atrial muscle degeneration
Right ventricular cardiomyopathy Cardiac Arrhythmia
Myocarditis Chronic bradyarrhythmia
Tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy Chronic tachyarrhythmia
BOX 21-4 Neurohormonal, Renal, and Cardiovascular Activities in Congestive
Heart Failure
Autonomic Increased release of tumor necrosis factor and other cytokines
Heightened sympathetic nervous system activity
Increase heart rate Renal
Augmentation of myocardial contractility Efferent arteriolar constriction (via angiotensin II)
Vasoconstriction Increased filtration fraction (ratio of glomerular filtration rate
Release of renin to renal plasma flow)
Blunting of arterial blood pressure reflexes Redistribution of renal blood flow
Increased sodium and water reabsorption
Hormonal or Autocrine
Vasoconstricting or sodium-retaining systems Cardiovascular
Activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system Cardiac adaptations
Release of arginine vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone) Ventricular dilatation
Release of vasoactive prostaglandins and local Ventricular hypertrophy
vasoconstricting factors Tissue changes (e.g., fibrosis, hypertrophy, altered
Endothelin-1 collagen matrix)
Thromboxane Cardiomyocyte death including apoptosis
Neuropeptide Y Intrinsic changes in cardiac isoenzymes
Vasodilating or natriuretic systems Down-regulation of cardiac b-receptors
Release of natriuretic peptides (impaired responsiveness of Vascular adaptations
end organ) Vasoconstriction
Increased basal nitric oxide (reduced release after receptor Increased systemic vascular resistance and arterial
stimulation) impedance
Increased release of prostaglandins (E 2 ,I 2 ) Redistribution of blood flow
Decrease in kallikreins Vascular remodeling
Increased dopamine
Decreased calcitonin gene-related peptide