Page 438 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 438
26.3 Ultrasonography 449
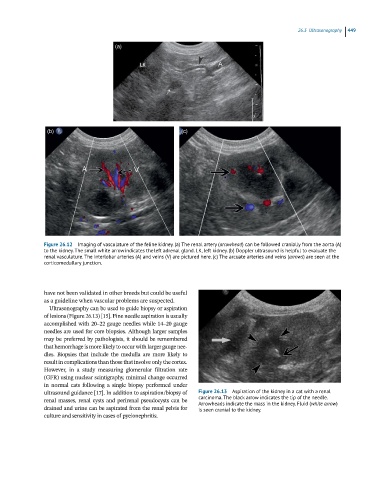
(a)
(b) (c)
Figure 26.12 Imaging of vasculature of the feline kidney. (a) The renal artery (arrowhead) can be followed cranially from the aorta (A)
to the kidney. The small white arrow indicates the left adrenal gland. LK, left kidney. (b) Doppler ultrasound is helpful to evaluate the
renal vasculature. The interlobar arteries (A) and veins (V) are pictured here. (c) The arcuate arteries and veins (arrows) are seen at the
corticomedullary junction.
have not been validated in other breeds but could be useful
as a guideline when vascular problems are suspected.
Ultrasonography can be used to guide biopsy or aspiration
of lesions (Figure 26.13) [15]. Fine needle aspiration is usually
accomplished with 20–22 gauge needles while 14–20 gauge
needles are used for core biopsies. Although larger samples
may be preferred by pathologists, it should be remembered
that hemorrhage is more likely to occur with larger gauge nee-
dles. Biopsies that include the medulla are more likely to
result in complications than those that involve only the cortex.
However, in a study measuring glomerular filtration rate
(GFR) using nuclear scintigraphy, minimal change occurred
in normal cats following a single biopsy performed under
ultrasound guidance [17]. In addition to aspiration/biopsy of Figure 26.13 Aspiration of the kidney in a cat with a renal
renal masses, renal cysts and perirenal pseudocysts can be carcinoma. The black arrow indicates the tip of the needle.
Arrowheads indicate the mass in the kidney. Fluid (white arrow)
drained and urine can be aspirated from the renal pelvis for is seen cranial to the kidney.
culture and sensitivity in cases of pyelonephritis.